Avocado is one of the most nutrient-dense foods you can eat every day. It combines healthy fats, fiber, phytosterols, electrolytes, vitamin C, vitamin E and almost all B vitamins with fewer than 85 calories per serving size! It can be part of any diet plan for weight loss, as it curbs cravings, helps increase metabolism, and protects muscle mass.
Nutritional Value
Avocados are rich in protein, fiber, various vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and various other beneficial phytochemicals.
| California avocado (per serving) | % DV | Florida avocado (per serving) | % DV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| calories | 84 | 4% | 60 | 3,0% |
| protein (g) | 1 | N/A | 1,1 | N/A |
| carbs (g) | 4,3 | N/A | 3,9 | N/A |
| fiber (g) | 3,4 | 12,1% | 2,8 | 10,0% |
| sugar (g) | 0,2 | 0,6% | 1,2 | 4,8% |
| fat (g) | 7,7 | N/A | 5,1 | N/A |
| SFA (g) | 1,1 | 8,2% | 1,0 | 7,5% |
| MUFA (g) | 4,9 | N/A | 2,8 | N/A |
| PUFA (g) | 0,9 | N/A | 0,8 | N/A |
| copper (mg) | 0,1 | 9,4% | 0,2 | 17,2% |
| vitamin C (mg) | 4 | 5% | 9 | 9,7% |
| pantothenic acid (mg) | 0,7 | 15% | 0,5 | 9,3% |
| vitamin E (mg) | 1 | 7% | 1,3 | 9% |
| folate (mcg) | 45 | 11,1% | 18 | 4,4% |
| potassium (mg) | 254 | 5,4% | 176 | 3,7% |
| magnesium (mg) | 15 | 3,5% | 12 | 2,9% |
| phosphorus (mg) | 27 | 4% | 20 | 3% |
| vitamin B6 (mg) | 0,1 | 8,4% | 0,04 | 2,3% |
| manganese (mg) | 0,1 | 3,3% | 0,05 | 2,1% |
| zinc (mg) | 0,3 | 3,1% | 0,2 | 1,8% |
| calcium (mg) | 6,5 | 0,7% | 5 | 0,5% |
| iron (mg) | 0,3 | 1,7% | 0,1 | 0,5% |
Remember that % DV represents the percentage of the recommended daily value based on a 2,000-calorie diet. Both California and Florida avocados offer unique nutritional benefits, so enjoy them as part of a balanced diet!
Individual avocados may vary slightly in nutrient composition.

What’s the serving size?
The typical serving size of an avocado is 50 grams, which is about 1/5 of a medium avocado. However, the actual serving size can vary depending on several factors, such as:
- The size of the avocado. Avocados come in a range of sizes, from small to extra large. Individual avocados can vary in size considerably.
- Hass; The most popular California avocado variety, typically weighing between 8-10 ounces (227-283 grams) when ripe. They have pear-shaped, bumpy skin that turns from green to black when ripe.
- Bacon: Slightly larger than Hass avocados, averaging 10-12 ounces (283-340 grams) at maturity. They have smooth, green skin with a long, slender neck.
- Choquette: The most popular Florida avocado variety, known for its large size and smooth, green skin. They can weigh anywhere from 16-24 ounces (454-680 grams) when ripe.
- Your individual needs. If you’re trying to lose weight, you might want to stick to a smaller serving size. On the other hand, if you’re very active, you might need a larger serving to meet your calorie needs.
- How you’re eating the avocado. If you’re eating the avocado on its own, a 50-gram serving is a good starting point. But if you’re adding it to other foods, such as a salad or sandwich, you might want to use less.
Can Avocado make you Gain Weight?
Avocado can make you fat, as it’s pretty high in calories. Just a small serving of 50 grams has about 84 calories.
Keep in mind that Florida avocados have approximately 34% less fat than California avocados!
| California avocado | Florida avocado | |
|---|---|---|
| 100g | 164 | 120 |
| whole fruit | 227 | 365 |
| half | 114 | 182 |
| serving (50g) | 84 | 60 |
| a slice | 27 | 19 |
Therefore, you shouldn’t consume too much avocado if you want to lose weight. We should be in a caloric deficit in order to lose weight. However, eating avocado in moderation can actually help us lose weight.
Avocado has the most calories per serving than any other common fruit, second only to coconut (354 calories per 100g). Only dried, dehydrated, or canned fruits may have more calories.
How many calories are in avocado-based foods?
- Guacamole, a favorite avocado-based dip, has 155 calories per 100g. A tbsp has 23 calories, while a typical serving (1/4 cup) has approximately 108 calories.
- An avocado toast with a medium egg has about 320 calories.
- Avocado salad (1 cup) has 200-400 calories depending on salad base, dressing, and other toppings.
- Avocado smoothie can have between 200 and 500 calories per serving. The calorie content depends on added ingredients like milk, yogurt, protein powder, fruits, and sweeteners.
- avocado sushi roll with salmon or tuna has 181 and 158 calories per 100g, respectively.
Avocado mayonnaise, dressing, sauce, and hummus are also high in calories.
But, above all, the most calorie-dense avocado product is avocado oil, containing 884 calories per 100g, or almost 125 calories per tbsp! It has such a high calorie content as it’s almost 100% fat. Actually, all vegetable oils are particularly high in fat. You should only eat small amounts. Especially, if you want to lose weight.

Tips for managing calorie intake with avocado-based foods:
- Be mindful of portion sizes, especially when using whole avocados.
- Choose lean protein and vegetable add-ins over calorie-dense options like cheese, fried toppings, or sugary fruits.
- Opt for healthier cooking methods like grilling, baking, or using raw ingredients.
- Track your calorie intake throughout the day to ensure avocado-based foods fit within your overall goals.
Remember, avocados are a healthy and nutritious food, but it’s essential to be mindful of portion sizes and ingredient choices to avoid exceeding your calorie goals.
What does Science say?
Whether regular avocado consumption leads to weight gain depends on various factors, including your overall diet, calorie intake, and individual metabolism. It’s important to look at the bigger picture beyond just one food item.
Research actually suggests potential benefits for weight management when avocados are incorporated into a healthy diet, though.
Study 1
A large cohort study with more than 55,000 participants found that avocado consumption was associated with lower body weight, BMI, and waist circumference, and decreased odds of becoming overweight or obese over time.[2]
Study 2
Another study among more than 17,000 US adults published in the Nutrition Journal investigated the relationship between avocado consumption and overall diet quality, nutrient intake, and metabolic syndrome risk. The study found that avocado consumers had a 50% lower risk of metabolic syndrome compared to non-consumers![3]
In addition, people who regularly ate avocado had lower body weight, BMI, waist circumference, and higher HDL-cholesterol (good cholesterol).
Study 3
A randomized trial showed that including Hass avocados in a weight-loss diet supported weight loss and altered gut microbiota in only 3 months.[4]
Study 4
According to another study, even the daily consumption of one avocado for six months, as part of a balanced diet won’t make you fat, despite its high-calorie content. Actually, avocado consumption appears to have favorable effects on body weight and belly fat burning in individuals with an increased waist circumference! In the U.S. approximately 60% of adults have visceral obesity.[5]
Study 5
Scientists tried to evaluate the effect of avocado intake on satiety. They found that just one half of a Hass avocado at a lunch meal can influence satiety for up to 5 hours. Overweight people who ate avocado increased satisfaction by 26% while decreased the desire to eat by 40%.[6]
Do avocados burn belly Fat?
Avocados have gained some attention for their potential role in weight management, including belly fat reduction. They can be a healthy addition to a weight management plan, but they are not a standalone solution for burning belly fat.
While they might offer some indirect benefits that could support this goal, it’s crucial to understand that there isn’t a magic food for burning belly fat alone.
The key role of Fiber in the Diet
Avocado is the richest common fruit in fiber, providing 5-8 grams per 100g. A serving provides more than 10% of the Daily Value.
For comparison, bananas and cranberries which are considered fiber-rich fruits have only 2.6 grams of fiber per 100g (60% less).
Benefits of Fiber on Weight Loss
Fiber absorbs water in the digestive system, making you feel fuller for longer and reducing the desire to snack frequently. Hence, consuming foods rich in fiber can lead to a decrease in spontaneous calorie intake at subsequent meals.
Also, it slows down the digestion of food, allowing nutrients to be released gradually into the bloodstream. This helps stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes and cravings.
Moreover, fiber influences the release of fullness hormones that increase satiety and regulate appetite.
Chewing and biting also play a role in satiety.
Increasing your daily fiber intake by 14 grams of fiber daily can reduce calorie consumption by up to 10%.
Avocados are a great keto-friendly fiber source!
Fiber in avocados could help people on keto meet their daily fiber needs. They’re keto-friendly food, as they have negligible amounts of sugar or starch while a serving provides 10% DV of fiber!
There aren’t many keto-friendly fruits. Only berries are other fruits that are suitable for a ketogenic diet plan.
People on keto may be at risk of fiber deficiency due to limited consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.[7]
Don’t Spike Blood Sugar
Furthermore, avocados won’t spike blood sugar. As they contain no sugar, their glycemic index is 0.
As they have such a low glycemic index, you could use them in your favorite recipes to lower the total glycemic load.
Meals with a low glycemic index are good for weight control. They tend to be more filling, prevent overeating, and reduce insulin secretion.[8]
Most noteworthy, low-glycemic index diets have been associated with a lower risk of heart disease by improving cholesterol levels, reducing inflammation, and promoting healthy blood pressure.[9,10]
Healthy Fats in Avocado support Weight Loss
We have to consume moderate amounts of healthy fats for good health. Low/moderate-fat diets help us lose weight and can reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Avocados can be a key part of a healthy, well-balanced diet for weight control.[11]
Saturated fat
A serving of avocado has only 1.1 grams of the “bad” saturated fat or 8% of the maximum safe intake.
The American Health Association suggests replacing foods high in saturated fats with foods containing monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fats. We shouldn’t consume more than 13 grams of saturated fat a day to protect the heart.[12]
The main source of saturated fat is animal products, such as meat and dairy. That’s a key reason why you should prefer low-fat milk, yogurt, or cheese.

Healthy fats
Avocados are mainly monounsaturated fatty acids, which are good for the heart when consumed in moderation. Avocado contains almost 10 grams of monounsaturated fat per 100g.
Monounsaturated fats in avocado are good for weight loss! They help the body burn more fat for energy, as they’re involved in energy metabolism. Also, they reduce appetite and increase insulin sensitivity.[13,14]
A diet rich in monosaturated fat seems to protect against abdominal fat accumulation, due to the regulation of certain fat genes. In other words, eating avocado, which is 72% monosaturated fats, helps maintain a flat stomach![15]
Hence, it’s probably better to follow moderate-fat diets, containing healthy fats from seeds, nuts, avocado, or olive oil, than restrict fat intake in total. Plant-based foods are the best sources of monounsaturated fats.[16]
Omega-3s
Last, but not least, avocado is the only fruit naturally rich in omega-3s which play an important role in health as well as weight control!
California-type avocados contain about 0.11 grams of omega-3s per 100g. This dose is about 7% of the recommended daily intake. In fact, whole fruit contains about 0.15 grams of omega-3s or more than 9% of the Daily Value![2]
Florida-type avocados have a slightly lower omega-3 content. They have only 0.096 grams of omega-3s per 100g. They contain 12% less omega-3s, as compared to California-type avocados.
Avocado oil contains decent amounts of omega-3s as well. Just a tablespoon has 0.13 grams of omega-3s. This dose is 8% of the DV.
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to play a role in weight management. While more research is needed, studies suggest that incorporating omega-3s into your diet may help with weight loss or maintenance.
Omega-3s can help regulate metabolism, reduce inflammation, and improve insulin sensitivity, all of which are factors that can impact weight.[44]
Also, they’re involved in skeletal muscle metabolism and protect the heart. They may improve endothelial function, reduce blood pressure, and significantly lower triglycerides.[45]

The key role of Vitamin E in Weight Control
Additionally, avocado is an excellent dietary source of vitamin E. It provides up to 9% DV per serving. Along with mangoes, kiwis, and blackberries, they are the richest fruits in vitamin E. In fact, other fruits contain negligible amounts.
Adequate amounts of vitamin E are necessary for weight loss. Among others, vitamin E decreases insulin resistance, manages glucose metabolism, and inhibits inflammation in the fat tissue.[17]
But, only a few foods are good sources of vitamin E.
Vitamin K helps burn belly fat
Also, avocado is a good source of vitamin K. A serving provides 9% of the DV. Vitamin K seems to influence body weight and body composition, as it significantly affects fat and glucose metabolism and helps reduce dangerous abdominal and visceral fat.[18]
Chicken and green leafy vegetables are among the best natural sources.
Avocados are packed with Antioxidants!
Chronic inflammation can contribute to excess body fat. Some studies suggest that avocados may help reduce inflammatory markers, potentially aiding weight management, as they increase the antioxidant capacity of the body.

Carotenoids
Carotenoids play a key role in body fat metabolism, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and inflammation. They help us control body weight and may affect body composition.[19]
Avocado is rich in carotenoids. It has 62 mcg beta-carotene, 24 mcg alpha-carotene, 271 mcg lutein and zeaxanthin per 100g! In fact, California Hass avocados have the highest content of lutein among commonly eaten fruits![20]
If you want to skyrocket your daily intake of carotenoids, you should eat sweet potatoes, carrots, and a wide variety of leafy greens!
The dark green flesh close to the skin has the highest carotenoid concentrations. So, it’s vital to peel avocados as thinly and as close to the skin as possible.
Phytosterols
Avocado is the richest common fruit in phytosterols with 57 mg per half (68 g) of the fruit. It has more than 3 times that of other fruits rich in phytosterols, such as oranges or apricots.[21]
Phytosterols are plant sterols structurally similar to cholesterol. Above all, they lower cholesterol absorption, causing the reduction of blood LDL-cholesterol levels. Increasing the intake of phytosterols is an easy way to reduce the risk of coronary heart disease.[22]
Furthermore, according to a 2018 study, consuming foods rich in phytosterols is beneficial for lower blood pressure, Body Mass Index (BMI), and waist circumference. Phytosterols seem to help the body burn more belly fat, and also decrease the risk of obesity![23]
Avocados contain up to 20 times more phytosterols than other common fruits!
A well-hydrated body helps burn belly fat
Being well-hydrated contributes to a healthy environment for weight management. Water contributes to a feeling of fullness, potentially reducing calorie intake. Sometimes thirst is mistaken for hunger. Staying hydrated helps differentiate between thirst and true hunger.
It also aids digestion, helping your body process nutrients effectively. When you’re well-hydrated, your cells function efficiently, including those involved in fat metabolism.
Dehydration can also affect energy levels and exercise performance, hindering weight management efforts.
Avocados hydrate the body, as they are 70-80% high-quality, purified water and they’re packed with essential electrolytes.
For instance, potassium and magnesium are important for various bodily functions, including fluid balance.
Drinking water without replenishing lost minerals could lead to electrolyte imbalances, which can have negative effects on many functions of the body. They’re implicated in the function of the nervous system and muscle contraction.
The main electrolytes are sodium, chloride, potassium, magnesium, and calcium.
Choose diverse hydrating foods: Fruits, vegetables, and even soups can contribute to fluid intake.
Potassium
Avocado is the richest common fruit in potassium. Certain California varieties contain more than 500 mg per 100g. Banana which is considered another excellent source has only 360 mg per 100g.
Potassium is present in all body tissues. It’s required for normal cell function, kidney function, and glucose metabolism.
Diets high in potassium may reduce the risk of diabetes, high blood pressure, stroke, and possibly other cardiovascular diseases. Especially when combined with low-sodium diets.[24,25,26]
In addition, potassium is involved in muscle contraction and nerve transmission. Furthermore, potassium may decrease the risk of developing osteoporosis and kidney stones, as it regulates calcium metabolism. Increased consumption of potassium is associated with increased bone mineral density and improved bone health.
California avocados can have 40% more potassium than bananas!
Magnesium
Avocado is one of the richest fruits in magnesium providing almost 4% of the Daily Value per serving.
It’s the fourth most abundant mineral in the body, acting as a cofactor for more than 300 enzymes!
Magnesium plays a role in weight management, as among others it’s involved in energy production, glycemic control, protein synthesis, and the production of anabolic hormones, and prevents water retention.
Furthermore, magnesium improves immunity, as it’s a key compound for the synthesis of glutathione, which is a powerful antioxidant.

Constipation
Furthermore, avocado may make you poop because it’s particularly high in magnesium. Magnesium may be effective for improving defecation status and shortening colonic transit time in people with mild to moderate constipation symptoms.[27]
Lutein and zeaxanthin in avocadoes seem to lower the incidence of constipation as well.[28]
Omega-3s may also have a beneficial effect on mild constipation issues. They act as natural lubricants and may improve bowel movement. In fact, a diet low in omega-3s may increase the risk of irritable bowel syndrome.[29]
Constipation can contribute to weight gain over time. It can sometimes cause discomfort or pain, which may lead to reduced physical activity, further contributing to weight gain. Additionally, chronic constipation can be a symptom of underlying health issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or thyroid problems, which can also affect weight management.
The importance of adequate Collagen levels
Did you know that avocado may improve collagen concentrations, as it’s packed with certain essential compounds for its synthesis?
For example, the naturally abundant copper in avocados (up to 17% DV per serving) is vital for collagen production.
Collagen is a protein crucial for skin, bones, muscles, and connective tissues, providing structure, support, and elasticity!
Collagen might support muscle maintenance during calorie restriction, which can help boost metabolism and burn more calories at rest.
Increasing collagen synthesis could help improve skin elasticity and firmness, potentially mitigating the appearance of sagging after rapid weight loss.
Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, losing only 1-2 pounds every week, quitting smoking, and practicing sun protection are also crucial for overall skin health.
Many Nutrients in Avocado play a role in Weight Control
Chromium
Also, avocado is one of the richest foods in chromium. This trace element seems to promote weight loss and reduce cravings for fattening foods! It’s implicated in the functions of insulin, and carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism!
B Vitamins
B vitamins support energy production, potentially influencing metabolism and energy levels that could indirectly impact weight management and support physical activity. Insufficient levels can lead to fatigue. A serving provides:
- pantothenic acid (up to 15% DV)
- folate (up to 11% DV)
- vitamin B6 (up to 9% DV)
- riboflavin (up to 6% DV) also
- niacin (up to 6% DV)
- thiamine (up to 3% DV)
Also, it’s important to note that B vitamins support homocysteine metabolism, which indirectly promotes cardiovascular health.
B vitamins protect the heart and increase energy levels.
Tryptophan
Also, avocado is a good dietary source of tryptophan; an essential amino acid that is involved in the synthesis of serotonin. This chemical reduces appetite and cravings and promotes nutrient absorption and storage. Also, it improves your mood.

How much avocado should I eat a day for weight loss?
A serving size is 50 grams (~1/5 avocado). But you could consume higher amounts if you enjoy it without gaining weight. A good starting point might be half a California avocado or 1/3 of a Florida avocado a day. This portion size provides about 120 calories.
Athletes and active people can eat a whole California avocado or half a Florida avocado per day and still lose weight because they have increased energy needs. This portion size provides 180–230 calories.
You can eat higher amounts while dieting, but you should regulate total calorie intake accordingly.
According to a study, even eating 11/2 avocado (200 grams) a day won’t make you fat. Especially if you eat avocado instead of other “less healthy” fats, coming from vegetable oils, margarine, or animal-derived foods![30]
Even a whole avocado a day is unlikely to make you fat.
How to Eat Avocado?
Combining avocados with certain foods to skyrocket the total nutritional value of a meal or snack.
With a Protein Source
Avocado is the richest common fruit in protein, but this isn’t enough. A serving provides only around 1 gram. So, it’s a good practice to eat avocado with a protein source, like lean meat, fish, egg, Greek yogurt, or beans.
Protein is a valuable tool in your weight loss journey, offering several benefits. Firstly, it takes longer to digest than carbohydrates or fats, keeping you feeling fuller for longer, which can lead to reduced calorie intake throughout the day. This can help you achieve a calorie deficit, essential for weight loss.
Digesting and processing protein requires more energy than other nutrients, leading to a slightly increased metabolic rate. This translates to burning more calories throughout the day, even at rest.
It’s important for muscle preservation as well. Losing weight often involves some muscle loss. During calorie restriction, your body might break down muscle for energy. Protein helps preserve muscle mass, which is crucial for maintaining metabolic rate and a lean body.
With Foods rich in Vitamin C
Avocado contains decent amounts of vitamin C (up to 10% DV per serving). But, as it’s crucial for fat metabolism, you’ll benefit from adding foods high in vitamin C to your avocado recipes.
Obese people may require significantly higher doses than the recommended daily intake to lose weight.
Hence, you could add lemon juice, tomatoes, or peppers to your avocado recipes to boost vitamin C intake.
With Calcium Sources
Avocado is a poor dietary source of calcium. A serving provides less than 1% DV.
Calcium is crucial for overall health and it appears to play an indirect role in weight control.
It might promote feelings of fullness, potentially leading to reduced calorie intake. Calcium provides small increases in thermogenesis, which is the body’s core temperature, leading to burning more calories at rest. Thus, adequate amounts of calcium while dieting might help improve body composition.
Hence, combining avocado with dairy products could enhance your weight loss efforts.
Cow’s milk and dairy aren’t the only good dietary sources of calcium. Plant-based foods, including kale, collard greens, arugula, beans, and chia seeds are rich in calcium as well.
With foods rich in Iron
Maintaining healthy levels of iron is important for good health and a lean body. Iron helps transfer oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and it’s involved in energy metabolism, neurological development, and the synthesis of some hormones, amino acids, and collagen.[31]
However, iron deficiency is the most common nutritional deficiency worldwide. It may lead to serious adverse effects, including weakened immune function, fatigue and decreased physical activity, potentially hindering weight loss efforts.[32]
Avocado has some iron (up to 2% DV per serving) but it isn’t considered an iron-rich food. Other fruits have substantially more iron than avocados.

Keep in mind that we absorb only a small percentage of iron in avocados and other plant-based foods. Phytates and polyphenols in plants inhibit its absorption. The bioavailability of iron from vegetarian diets is between 5% and 12%, while the bioavailability of iron from mixed diets is up to 18%. Therefore, it’s highly recommended that vegetarians consume 1.8 times more iron than people who eat meat.
Common foods high in iron are meat, poultry, fish, eggs, whole grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, potatoes, dark chocolate, and certain vegetables and fruits. Meat and fish contain heme iron, which enhances non-heme (the iron in plants) iron absorption.
You can eat avocadoes with fermented foods like tempeh and tofu. They are good sources of bioavailable iron due to the fermentation process.
Above all, you can increase the absorption of iron in avocados by cooking them with foods rich in vitamin C, like lemon juice.
Vitamin C can increase nonheme iron absorption by up to 270%.
With foods rich in Zinc
Zinc may play a role in regulating insulin, potentially leading to better blood sugar control. This could indirectly impact weight loss by reducing cravings and promoting satiety.
Zinc could influence appetite hormones, potentially leading to reduced calorie intake. However, further reasearch is need in topic.
Avocados contains some zinc (up to 3% DV). You could prepare snacks with other zinc-rich foods, like beans, seeds, nuts, and lean meat.
With foods rich in Vitamin B12
Although avocado is packed with many B vitamins that play a crucial role in energy metabolism, as all common plant-based foods, it contains no vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12 supports numerous functions, including energy production, red blood cell formation, and nervous system function. A deficiency can lead to fatigue, weakness, and anemia, impacting energy levels and potentially hindering weight loss efforts indirectly.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is pretty common, especially among vegetarians, as only animal foods are good sources.
If you have a B12 deficiency, getting your levels to the recommended range through dietary changes or supplements can improve your energy levels and indirectly support weight loss efforts by encouraging physical activity. Keep in mind that, this is a corrective measure, not a weight loss strategy.
Among the most common deficiencies worldwide are vitamin B12 and vitamin D deficiency. You could find a wide variety of supplements at unbeatable prices on iHerb.
Gut Health
The gut microbiome, the community of trillions of bacteria residing in your intestines, plays a complex role in human health, potentially influencing weight management in several ways.
For instance, certain gut bacteria may influence how your body extracts energy from food and regulates metabolic processes, potentially impacting calorie burning.
Additionally, gut bacteria produce hormones and signals that communicate with the brain, potentially affecting feelings of hunger and fullness influencing food intake.
A healthy gut microbiome might contribute to decreased inflammation, potentially improving overall health and potentially aiding weight management. Chronic inflammation is linked to obesity and metabolic disorders.
Avocado consumption can improve gut health. It helps reduce the population of bad gut bacteria, while increasing the beneficial ones.[4]
Dietary fiber and monounsaturated fats in avocados have beneficial effects on the gastrointestinal microbiota. Regular avocado consumption can increase the diversity and population of beneficial bacteria within the gut microbiome, such as Faecalibacterium, Lachnospira, and Alistipes by up to 65%.[33]
Among others, these beneficial bacteria support the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and other metabolites, which provide energy for gut cells, reduce inflammation, and may improve insulin sensitivity.
How to get more Avocados in your Diet
Consuming avocado daily is easy. Here are 22 delicious ways to boost your avocado intake:
Breakfast:
Avocado Toast: The classic! Mash avocado on whole-wheat toast and top with your favorite toppings like poached eggs, smoked salmon, feta cheese, or chili flakes.
Avocado Smoothie: Blend avocado with spinach, banana, and your favorite milk for a creamy and filling smoothie. I use kefir instead of milk, as it’s the richest food in probiotics and enhances weight loss.
Breakfast Scramble: Add diced avocado to scrambled eggs with chopped vegetables and cheese.
Avocado Oatmeal: Top your oatmeal with sliced avocado for a creamy and healthy twist.
Lunch & Salads:
Avocado Salad: Combine avocado with leafy greens, chopped vegetables, grilled chicken or fish, and a light vinaigrette. Monounsaturated fats in avocados significantly enhance the bioavailability of carotenoids in vegetables, such as lutein and alpha-carotene.[34]
Stuffed Avocado: Scoop out the flesh of the avocado and fill it with quinoa, black beans, corn, salsa, and a squeeze of lime.
Avocado Tuna Salad: Mix mashed avocado with tuna, celery, red onion, and light mayonnaise for a healthy and delicious sandwich filling.
Chicken or Tofu Salad with Avocado: Add sliced avocado to your favorite chicken or tofu salad recipe for extra creaminess and healthy fats.

Snacks & Side Dishes:
Guacamole: The ultimate avocado dip! Enjoy it with whole-wheat tortilla chips, vegetable sticks, or even spread on toast.
Avocado Slices with Lemon & Spices: Sprinkle avocado slices with a squeeze of lemon, salt, pepper, and chili flakes for a simple and satisfying snack.
Deviled Eggs with Avocado: Replace some of the mayonnaise in your deviled egg filling with mashed avocado for a healthy twist.
Hummus & Avocado Dip: Combine mashed avocado with hummus for a protein-packed and flavorful dip.
Avocado & Black Bean Dip: Blend avocado, black beans, cumin, and lime juice for a delicious and healthy dip.
Main Dishes:
Creamy Avocado Pasta Sauce: Blend avocado with basil, garlic, lemon juice, and Parmesan cheese for a healthy and flavorful pasta sauce.
Avocado Burgers: Add mashed avocado to your burger patties for added moisture and flavor.
Stuffed Peppers with Avocado & Quinoa: Fill bell peppers with cooked quinoa, black beans, corn, and diced avocado for a hearty and healthy meal. Quinoa is a superfood for weight loss.
Avocado and Shrimp Tacos: Top corn tortillas with grilled shrimp, sliced avocado, cabbage, and a creamy avocado sauce.
Desserts & Sweets:
Avocado Chocolate Mousse: Blend avocado with cocoa powder, honey, and almond milk for a healthy dessert.
Avocado Ice Cream: Blend frozen avocado with cocoa powder, honey, and almond milk for a creamy and refreshing treat.
Avocado and Fruit Smoothie Bowl: Blend together avocado, frozen banana, yogurt, and your favorite fruits for a delicious and nutritious smoothie bowl. Banana has so many benefits for weight loss, especially when combined with a protein source like Greek yogurt.
Chia Seed Pudding with Avocado: Top your chia seed pudding with sliced avocado and berries for a healthy and satisfying snack.
Avocado Banana Bread: Add mashed avocado to your favorite banana bread recipe for added moisture and healthy fats.
Bonus Tip: Purchase unripe avocados and ripen them at home. This allows you to choose avocados that perfectly fit your consumption schedule.
When should I eat avocado to lose weight?
There isn’t one definitive “best” time to eat avocado for weight loss. You can consume it at breakfast, lunch, dinner, or after the gym.
I prefer eating it in the morning, as it keeps me full for many hours. It reduces hunger for up to 5 hours. It helps me consume fewer calories at lunch.[6]
At Dinner
A good night’s sleep plays a crucial role in weight management. When you’re well-rested, your body regulates hormones like leptin and ghrelin, which control hunger and satiety. Insufficient sleep can disrupt these hormones, leading to increased appetite and cravings.
Additionally, lack of sleep can affect your metabolism and energy levels, making it harder to burn calories and stay active. Quality sleep is essential for overall health and well-being, and it’s an often overlooked factor in weight loss and maintenance.
Serotonin
Avocado consumption before bed may help improve sleep quality and duration because it’s a good dietary source of serotonin. Serotonin is a biosynthetic precursor of melatonin. Melatonin is also known as the sleep hormone. It regulates sleep.
Fruits, vegetables and seeds are the main dietary sources of serotonin. Stress, increasing age, insulin resistance, and magnesium and vitamin B6 deficiency may negatively affect the synthesis of serotonin.[34]
Magnesium & Vitamin B6
Also, avocado contains decent amounts of magnesium and vitamin B6. A whole Hass avocado provides 9% of the Daily Value of magnesium and 30% of the DV of vitamin B6!
Zero Glycemic Index
Moreover, avocado controls glycemic responses. It may improve insulin sensitivity, which is also vital for the synthesis of serotonin! Avocado doesn’t spike blood sugar levels, as it has a glycemic index of zero!
Diets rich in complex carbohydrates (e.g., fiber) and healthy fats have been associated with better sleep quality. On the contrary, it seems that the consumption of high amounts of simple carbs close to bedtime is accompanied by frequent arousal and may affect sleep quality[35,36]
Tryptophan
Furthermore, avocado is among the richest fruits in tryptophan. It contains 25-28 mg of tryptophan per 100g. A whole Florida avocado contains 85 mg of tryptophan. This amount is 20-34% of the DV.
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that is necessary for the synthesis of niacin and serotonin. It has been used for the treatment of sleep disorders for years. It seems to have beneficial effects on sleep latency and obstructive sleep apnea.[37]
Folate, Omega-3s, Potassium
High amounts of folate in avocados may also help people with sleep disorders and may relieve the symptoms of sleep deprivation.[38]
Omega-3s may improve sleep duration and protect against chronic sleep-deprivation side effects as well.[39,40]
Potassium in avocado may also improve sleep quality.[41]
Dopamine
Furthermore, avocado is a great dietary source of dopamine. It has 4–5 mcg of dopamine per gram. A whole Hass avocado has approximately 540-680 mcg of dopamine.[42]
Dopamine is one important sleep modulator. It plays an important role in the regulation of sleep. It’s involved in the function of neurons.[43]
After Exercise
Vitamin E
Vitamin E in avocados (11% DV per serving) has powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Athletes with low levels of vitamin E have an increased risk of developing exercise-induced inflammations in the muscles. This could have detrimental effects on physical performance and muscle recovery.
However, although vitamin E is beneficial for athletes, too much could negatively affect the synthesis of anabolic hormones and impair adaptations to resistance training. Therefore, athletes should get vitamin E only from their diet, not supplements. Sunflower seeds and almonds are the other two common foods high in vitamin E that you could include in your post-workout meal.[44]
Folate
Intense exercise may acutely increase the homocysteine levels. High homocysteine is dangerous for the health. Folate (22% DV) in avocados protects the heart, as it reduces elevated homocysteine levels. It may protect athletes against alterations that can lead to cardiovascular events![45]
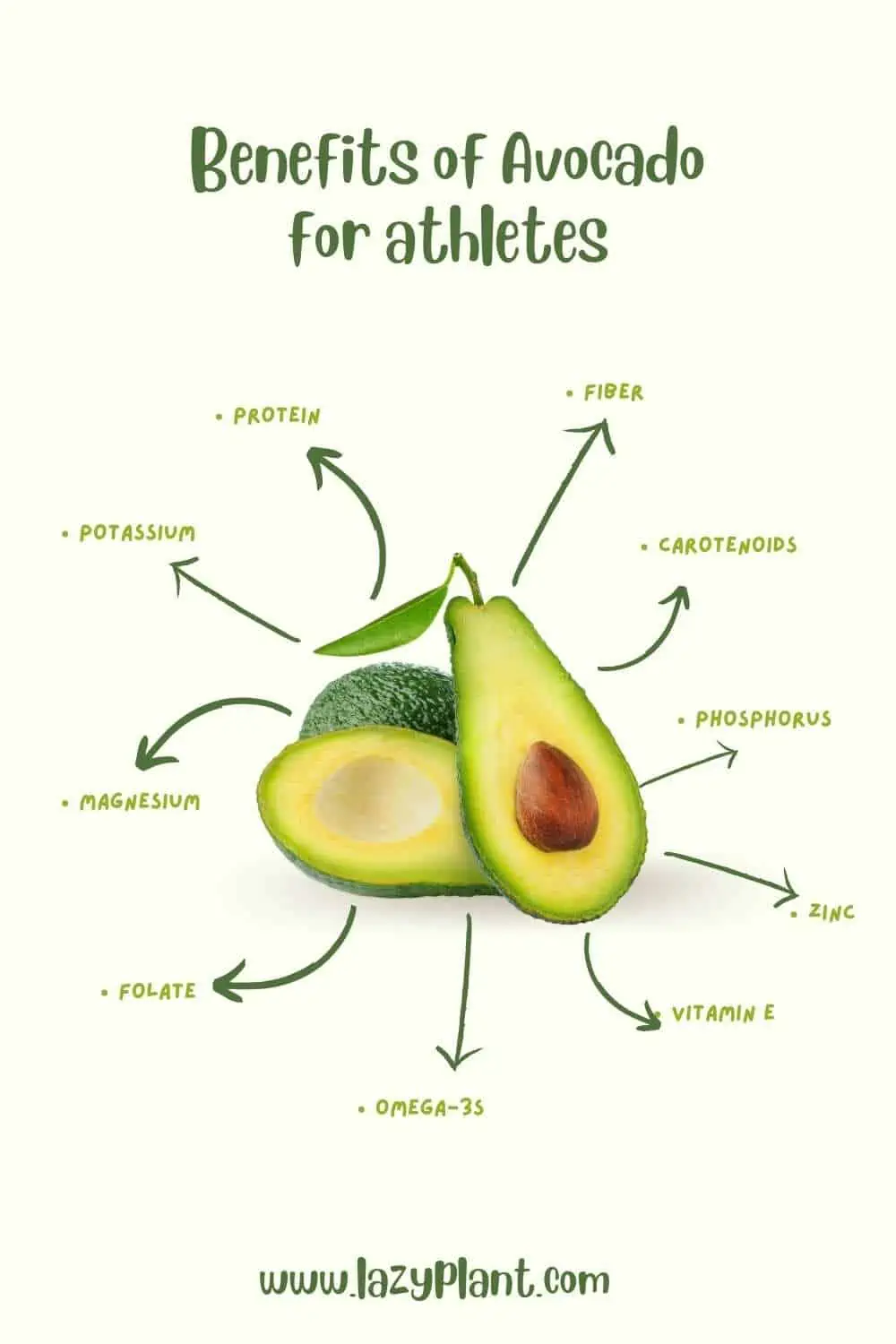
Minerals
Elite athletes have increased magnesium needs! It’s involved in glucose metabolism, delays lactate accumulation in the muscle, and has a protective effect on muscle damage. Avocado (6% DV) is the richest fruit in magnesium. It has more magnesium even than a banana![46]
Potassium plays a crucial role in muscle contraction and nerve function. Athletes who engage in intense workouts can deplete their potassium levels, leading to fatigue and cramps. Consuming avocado after exercise helps replenish potassium reserves, ensuring proper muscle function and preventing electrolyte imbalances.[47]
Iron is another essential mineral for athletes, as it is involved in oxygen transport and energy metabolism. Female athletes, especially those of reproductive age, are at a higher risk of iron deficiency. Avocado, being a rich source of iron, can help replenish iron stores and support overall athletic performance.
Also, athletes have increased zinc requirements due to the demands of their training. Zinc is vital for protein synthesis, muscle growth, and energy metabolism. Avocado, with its significant zinc content, can contribute to meeting these elevated needs.[48]
Avocado provides a good amount of phosphorus, supporting bone health and overall athletic performance.
Avocados are also rich in carotenoids, such as lutein and zeaxanthin. These antioxidants can help speed up muscle recovery and protect against exercise-induced muscle damage. They may even support muscle growth and strength.[49]
Can be eaten on an empty stomach?
Most people can eat avocado on an empty stomach. It doesn’t spike blood sugar levels as it’s low in net carbs and has a glycemic index of 0.
Avocados can slightly increase stomach acidity, though. While generally not a problem for most, it might trigger heartburn or indigestion in individuals prone to such issues, especially when consumed on an empty stomach.
Pairing avocado with protein, fiber, or carbohydrates can slow down digestion and potentially reduce discomfort.
How often can I eat avocado while dieting?
If your calorie goals allow, you can enjoy a moderate serving of avocado daily.
Regularly incorporating avocado into your diet as part of balanced meals and snacks can offer potential benefits for overall health and potentially aid weight management efforts. Certainly, it isn’t necessary to eat avocado every day:
- 3-4 times a week: This frequency might be suitable if you have lower calorie requirements or prefer variety in your diet.
- 2-3 times a week: This is a reasonable option if you want to enjoy avocado’s benefits while keeping an eye on portion control.
Don’t rely solely on avocado for weight loss. Focus on a sustainable lifestyle that includes healthy eating, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep.
Who should avoid consuming Avocado?
Certain individuals may need to be cautious or limit their avocado consumption.
Firstly, patients who follow a potassium-low diet better avoid it. Avocado is one of the richest foods in potassium.
If you have a known avocado allergy, avoid consuming it. Allergic reactions can range from mild (itching, hives) to severe (anaphylaxis).
If you have a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or other digestive issues, monitor how avocados affect you. Some individuals may find them triggering.
Some people with latex allergy may experience cross-reactivity with avocados. If you react to latex, monitor your response to avocados.
Avocados contain vitamin K, which can interact with blood-thinning medications like warfarin.
If you take medication or have certain health issues, consult your doctor about adjusting your avocado intake.
Ripe or unripe avocados for weight loss?
Both ripe and unripe avocados can be part of a healthy weight loss diet, as long as you consider their calorie and nutrient content and ensure they fit within your calorie goals.
Ripe avocados contain more monounsaturated fats, including oleic acid, which has been linked to various health benefits like improved satiety and possibly even increased calorie burning. They also offer slightly more vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Unripe avocados have slightly fewer calories and more fiber, which can promote satiety and gut health. Unripe avocados have a firmer texture and less pronounced flavor, which might not be as appealing to everyone.
Choose the one you enjoy more to ensure you’re incorporating it consistently into your diet.
Is it worth the Cost?
Avocados are generally considered a premium ingredient. They can be more expensive than other fruits and vegetables, especially depending on location, season, and quality. Prices can fluctuate, though.
Buying in season and choosing less ripe avocados can bring down the cost.
Moderate intake can help justify the higher cost per serving.
Certainly, a healthy diet doesn’t have to rely solely on expensive ingredients. You can incorporate various affordable options to achieve a balanced and nutritious lifestyle.
Other fruits and vegetables offer similar nutrients:
- healthy fats: nuts, seeds, olive oil, fish
- fiber and vitamins: various other fruits, vegetables, and herbs
How to choose the best one?
Choosing the best avocado depends on your needs and when you plan to use it.
For immediate consumption (within 1-2 days):
- Color: Look for dark green to almost black avocados, avoiding ones with green or yellow patches.
- Feel: Gently press the avocado near the stem. It should give slightly but not feel mushy. Avoid avocados that are hard or have dents.
- Stem: The stem should be brown and slightly loose. A green or tightly attached stem indicates an unripe avocado.
For later use (3-5 days):
- Choose firmer avocados: Select avocados with a deep green, unyielding skin and a tight stem.
- Ripening at home: Place unripe avocados at room temperature until they soften to your desired ripeness. You can speed up the process by placing them in a paper bag with ripe bananas or apples.
Avoid avocados that are bruised, dented, or have soft spots or mold. Choose avocados that feel heavy for their size, indicating denser flesh.
How to store it for longer
Keep ripe avocados in the refrigerator to slow down ripening. Once opened, they can be stored for 1-2 days by wrapping tightly in plastic wrap.
Are other favorite Fruits more beneficial for Weight Loss?
Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein for effective weight management. All fruits can have a place in a healthy, well-balanced diet. The best ones are those you actually eat.
| Fruit | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Avocado | healthy fats, fiber, phytosterols, carotenoids, electrolytes, vitamins supports gut health and digestion | Higher in calories per serving can be more expensive |
| Berries | low in calories high in fiber rich in antioxidants and vitamins | lower in healthy fats can be more expensive per serving (depending on type) |
| Citrus fruits | vitamin C and fiber | higher in sugar than some other fruits can be acidic and not suitable for everyone |
| Apples | high in fiber for satiety low in calories | lower in healthy fats and some other micronutrients less versatile in culinary use |
| Bananas | good source of potassium and other essential minerals easily portable and convenient snack provides quick energy | higher in sugar than some other fruits can ripen quickly and become mushy may not be suitable for everyone on low-carb diets |
Is Avocado actually a Superfood?
While avocados undoubtedly deserve a place among healthy and nutritious foods and can be part of any diet plan, you shouldn’t see them as a superfood. A healthy diet with a variety of health-promoting foods is far more important for good health and getting the body of your dreams.
“Superfood” is often used as a marketing term. There is no wonder why the supposed exotic, superfoods are so expensive!
10+1 Myths
Myth: Avocados are fattening. Reality: While avocados are higher in calories than some fruits due to their healthy fats, they are still considered a nutrient-dense food. These fats can actually offer health benefits like improved heart health and satiety. Moderation is key.
Myth: You should avoid avocados if you have high cholesterol. Reality: The healthy fats in avocados, specifically monounsaturated fats, can actually help lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol. Consult your doctor if you have specific concerns, but avocados generally don’t worsen cholesterol levels.
Myth: Avocados are only good for guacamole. Reality: Avocados are incredibly versatile! You can enjoy them in various ways, from mashed on toast to blended in smoothies, added to salads or stir-fries, or even used in desserts like chocolate mousse.
Myth: You can eat as many avocados as you want for weight loss. Reality: While avocados offer some benefits for weight management due to their fiber and healthy fats, they are still calorie-dense. Overindulging can hinder your weight loss goals. Stick to moderate portions.

Myth: You should only eat ripe avocados. Reality: Unripe avocados have firmer flesh and a less pronounced flavor. They can be used in different ways.
Myth: Avocados are a good source of protein. Reality: Avocados are not a significant source of protein.
Myth: All avocados taste the same. Reality: Different avocado varieties have distinct flavors and textures. Some are buttery and mild, while others are slightly grassy or nutty. Explore different varieties to find your favorites.
Myth: Avocados are bad for the environment. Reality: Like any agricultural product, avocado production can have environmental impacts. However, sustainable farming practices can reduce water usage and carbon footprint. Look for avocados from responsible sources whenever possible.
Myth: Avocados make you sleepy. Reality: There’s no scientific evidence to link avocado consumption to drowsiness. The healthy fats in avocados can even provide sustained energy.
Myth: Avocados will give you bad breath. Reality: Avocados themselves shouldn’t cause bad breath unless they are particularly ripe or spoiled. Maintaining good oral hygiene is always crucial.
Myth: Avocados can cure diseases. Reality: While avocados offer valuable nutrients, they are not a magical cure for any specific disease. A healthy lifestyle and proper medical treatment are key to managing health conditions.
10 Fun facts about Avocado!
Ancient Origins: Avocados have been cultivated for over 8,000 years, with evidence found in Central America dating back to 7,000 BC! They were even considered a sacred food by the Aztecs and Mayans.
More Than Just Green: While the classic green Hass avocado is most popular, over 500 varieties exist, with diverse colors like purple, black, and even red!
Not Technically a Fruit: Avocados belong to the Lauraceae family, making them closer relatives to cinnamon and bay leaves than to other fruits. Their large pit and fleshy center technically classify them as berries.
Guacamole Goes Global: The word “guacamole” comes from the Nahuatl language spoken by the Aztecs and translates to “avocado sauce.” Today, it’s a beloved dip enjoyed worldwide.
Record Breakers: The heaviest avocado ever recorded weighed over 5 pounds (2.5 kg)!
Tree Huggers: Avocado trees can live for 100 years or more, becoming impressive giants in their natural habitats.
Rainforest Rescue: Sustainable avocado farming can help protect rainforests by providing economic alternatives to deforestation.
Skincare Secret: Avocado oil is used in various skincare products due to its moisturizing and potentially anti-inflammatory properties.
A Global Phenomenon: From trendy cafes to home kitchens, avocados have become a global ingredient, enjoyed in diverse culinary cultures.
Sustainable Future: Research focuses on developing drought-resistant and high-yielding avocado varieties for more sustainable production.
Always consult your healthcare provider before changing your diet plan or taking dietary supplements. Especially if you take drugs or have health concerns.