Quinoa is a superfood for weight loss. Due to its superior protein, fiber, antioxidant, and mineral content, quinoa controls cravings, regulates glucose responses, helps build muscle mass, and improves body composition.
Nutritional Value of Quinoa
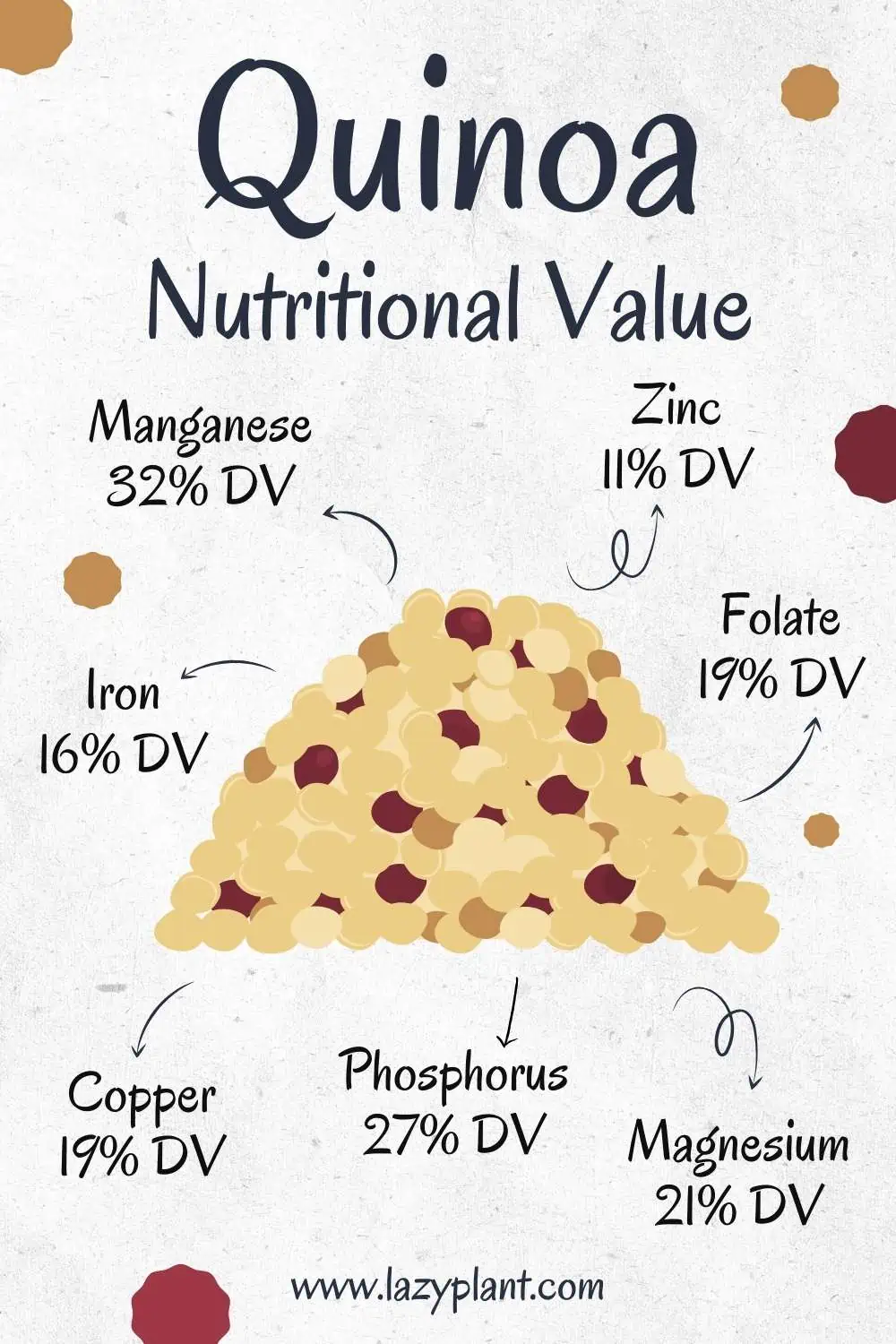
Quinoa is a pseudocereal. It’s a great dietary source of protein, fiber, and many minerals, such as phosphorus, magnesium, manganese, iron and zinc, as well as many vitamins that are implicated in energy metabolism.
| Nutrient | 100g | 1 cup (185g) | % DV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 71.6g | 132g | 85% |
| Energy | 120 kcal | 222 kcal | 11% |
| Protein | 4.4g | 8g | 16% |
| Total lipid (fat) | 1.92g | 3.5g | 5% |
| Carbs | 21.3g | 39g | 13% |
| Fiber | 2.8g | 5.2g | 14% |
| Total Sugars | 0.87g | 1.6g | 1% |
| Starch | 17.6g | 32.7g | 36% |
| Calcium, Ca | 17mg | 30mg | 3% |
| Iron, Fe | 1.49mg | 2.73mg | 16% |
| Magnesium, Mg | 64mg | 116mg | 21% |
| Phosphorus, P | 152mg | 277mg | 27% |
| Potassium, K | 172mg | 317mg | 6% |
| Sodium, Na | 7mg | 13mg | 1% |
| Zinc, Zn | 1.09mg | 1.98mg | 11% |
| Copper, Cu | 0.192mg | 0.35mg | 19% |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.631mg | 1.16mg | 32% |
| Selenium, Se | 2.8µg | 5.2µg | 5% |
| Thiamin | 0.107mg | 0.196mg | 10% |
| Riboflavin | 0.11mg | 0.20mg | 11% |
| Niacin | 0.412mg | 0.75mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B-6 | 0.123mg | 0.227mg | 8% |
| Folate | 42µg | 77µg | 19% |
| Choline, total | 23mg | 42mg | 10% |
The % Daily Value (DV) is based on a 2,000-calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower depending on your calorie needs.
The recommended serving size of cooked quinoa is a cup (185 grams).
It’s packed with Antioxidants
Besides being rich in essential minerals and vitamins, quinoa is also packed with powerful antioxidant compounds.
It’s particularly rich in flavonoids, including quercetin and kaempferol. Other flavonoids found in quinoa include orientin, vitexin, rutin, morin, hesperidin, and neohesperidin.[2]
Furthermore, at least 13 phytoecdysteroids have been identified in quinoa. Their total content ranges from 38 to 570 μg/g. These phytochemicals appear to have potent antioxidant actions.
The most predominant phytoecdysteroid (62–90%) in quinoa is 20HE. It exhibits antiobesity and antidiabetic activities!
According to studies, among others, 20HE has been found to prevent obesity, improve insulin resistance, and significantly decrease body fat mass.
Promising data also shows that it stimulates protein synthesis and muscle growth, promoting a lean body! In fact, researchers believe that quinoa is an excellent nutrient source for body recovery. Thus, athletes and fitness enthusiasts better incorporate it into their post-workout meals.
Additionally, a purified polysaccharide from quinoa seems to prevent fat cells from forming by stopping the genes that control fat cell formation from being activated.
Phenolic compounds in quinoa also help reduce the absorption of energy.
Quinoa can play a crucial role in increasing energy expenditure while reducing fat absorption.
Which is the healthiest variety?
Quinoa comes in three main varieties: red, black, and white. All three types of quinoa are healthy and nutrient-dense, but there are some differences between them.
White quinoa is the most commonly consumed variety.
Black quinoa is crunchy and has a strong nutty flavor. It contains more antioxidants than white quinoa. The total phenolic content of quinoa is affected by the color, genotype, and growth conditions.

All three types of quinoa are considered to be highly bioavailable.
Choosing which variety to consume mainly depends on personal preference and taste:
- Taste: If you prefer a milder flavor, white quinoa is a good choice. If you want a more nutty flavor, red or black quinoa is a better option.
- Cooking time: If you are short on time, white quinoa is the quickest variety to cook. If you don’t mind waiting a few extra minutes, red or black quinoa will offer more nutrients.
- Appearance: White quinoa is the most visually appealing variety. If you want a colorful dish, red or black quinoa can add a pop of color.
Benefits of Quinoa for Weight Loss
Protects Lean body mass due to its high Protein content
A cup of cooked quinoa contains 8.1 grams of protein.
Quinoa is one of the few plant-based foods that is a complete protein. It contains all 9 essential amino acids. Actually, quinoa has a great amino acid profile.[3]
The amino profile of quinoa may greatly defer, though. It depends on the quinoa variety, growing methods, soil, and processing methods. There are quinoa varieties that have less leucine, lysine, and tryptophan.
| % protein | grams per 100g | |
| Histidine | 2,66 | 0,12 |
| Isoleucine | 4 | 0,18 |
| Leucine | 6,25 | 0,28 |
| Lysine | 5,72 | 0,25 |
| Methionine | 2,17 | 0,10 |
| Phenylalanine | 3,9 | 0,17 |
| Threonine | 3,57 | 0,16 |
| Tryptophan | 1,08 | 0,05 |
| Valine | 4,78 | 0,21 |
It can even used as a healthy plant-based alternative to milk proteins.[4]
The protein quality of quinoa is compared to that of casein, which is considered to be among the best sources of protein. Especially for building muscle mass, as it’s easily digestible. Casein and quinoa proteins have almost the same biological value and digestibility.[5]
Even saponins of quinoa, which are anti-nutrient, plant-derived chemicals don’t inhibit protein absorption of quinoa.[6]
Hence, vegans and vegetarians could have huge benefits in consuming this functional food.
Other vegan sources of common complete protein sources are chia seeds, hemp seeds, pumpkin seeds, amaranth, spirulina, and buckwheat.
Why should I eat protein-packed foods while dieting?
Following a high-protein diet while dieting can have several benefits, including:
- Increased satiety: Protein is more satiating than carbohydrates or fats, which means it can help you feel full and satisfied for longer, leading to reduced overall calorie intake.
- Improved body composition: A high-protein diet can help you preserve muscle mass while losing fat, which can improve your overall physique.
- Increased metabolism: Protein has a higher thermic effect on food than carbohydrates or fats, which means your body burns more calories digesting and processing protein. We burn 20-30% of calories of protein during digestion!
- Reduced cravings: Protein can help reduce cravings for unhealthy snacks, making it easier to stick to your diet.
- Improved mood: Protein can help improve mood and reduce stress levels.
Hence, it’s advised to consume quinoa with a protein source, such as lean meat, eggs, seafood, or beans.
Promotes Satiety
After all, quinoa is an excellent source of fiber. A serving provides 14-18% DV. Meals containing both high amounts of fiber and protein have the highest satiety effect.[6]
Fiber
Quinoa contains both soluble and insoluble fiber. It’s mainly (78%) insoluble fiber, though. Soluble fiber helps to lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar, while insoluble fiber promotes digestive health and adds bulk to stool.[7]
Insoluble fiber doesn’t dissolve in the water. It absorbs water, making the stool softer. It helps defecation. On the contrary, soluble fiber dissolves in the water, turning into a gel. It slows down digestion and promotes satiety, promoting weight loss.
It has a low Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) of quinoa is between 50 and 54. It varies depending on the cooking method and variety of the quinoa. White quinoa has a slightly lower glycemic index than red quinoa. White quinoa cooked in boiling water for 15 minutes has a GI of 50, while the GI of boiled red quinoa is 54.[8]
Despite its relatively high carbohydrate content, quinoa has a low glycemic index because it’s high in fiber and protein, which slow down the process of digestion and gastric emptying.
Saponins, 20HE, phenolic, tocopherols and other bioactive peptide contents in quinoa have hypoglycemic potential and manage glucose responses. Quinoa has antidiabetic actions.[9]
Quinoa could help you manage body weight and stay healthy, even if you don’t follow a well-balanced diet. For instance, it can reduce certain adverse effects due to the overconsumption of fructose on glucose levels.[10]
Foods with a low GI release sugar into the bloodstream slowly, preventing blood sugar spikes. This can help you feel fuller for longer and reduce cravings for unhealthy snacks.
Additionally, when you eat foods with a low GI, your body burns more fat for energy. This is because your body doesn’t need to produce as much insulin to process the sugar, which frees up your body to use fat for fuel.
Here are some additional tips for following a low GI diet:
- Look for foods that have a GI of 55 or lower.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains.
- Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Limit processed foods and sugary drinks.
The role of Crunchiness
Another way quinoa keeps you full for hours is because it’s crunchy.
Crunchy foods require more chewing than soft foods, which can help you eat more slowly and mindfully. This can lead to greater satiety and a reduced risk of overeating. When you eat crunchy foods, your body releases hormones that signal to your brain that you are full.[11]
Moreover, when you focus on the textures and sounds of crunchy foods, you may be less likely to mindlessly overeat.
Supports Gut Health
Quinoa has probiotic properties. Fiber supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. It may help to increase the diversity and abundance of gut microbes, including Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus-Enterococcus.
Polysaccharides, proteins, and phenolic compounds found in quinoa also play a beneficial role. They promote the production of short-chain fatty acids, which regulate gut pH and overall microbiota composition.
The gut microbiome helps break down food, absorb nutrients, and regulate the release of hormones that control appetite and metabolism. An imbalance in the gut microbiome can impair these processes, leading to weight gain.
Also, it influences energy expenditure by producing short-chain fatty acids, which can increase metabolism and promote fat burning.
In addition to fiber, probiotics are also beneficial for gut health. The richest common food in probiotics is kefir, which is particularly beneficial for your weight loss journey!
Supports Fat Metabolism
- Manganese may support fat metabolism by helping break down fats into energy.
- Phosphorus is involved in the production of ATP, the energy currency of cells, which is essential for fat metabolism.
- Magnesium plays a role in protein synthesis, which is needed for muscle growth and repair, and both muscle mass and activity levels are important for fat metabolism.
- Copper is involved in electron transport, a crucial process in energy production, which is essential for fat metabolism.
- Zinc is involved in the production of enzymes that break down fats, which is essential for fat metabolism.
Helps burn belly Fat
- Magnesium may help burn belly fat by improving insulin sensitivity, which can help reduce sugar cravings and promote fat burning.
- Chromium may help burn belly fat by regulating blood sugar levels and reducing insulin resistance.
- B vitamins, particularly thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin, may help burn belly fat by supporting energy production and metabolism.
Manages Cravings
- Manganese may help reduce appetite and cravings by regulating neurotransmitters involved in hunger and satiety.
- B vitamins, particularly thiamine and folate, may help reduce cravings by supporting healthy brain function and mood regulation.
- Copper may help reduce cravings by reducing inflammation, which can contribute to increased appetite.
- Zinc may help reduce cravings by regulating the release of appetite hormones.
Fights Fatigue
Iron deficiency is a common nutritional deficiency worldwide, with fatigue and weakness to be common symptoms. It is required for the production of hemoglobin and myoglobin, which are proteins that help carry oxygen throughout the body and to the muscles, respectively. Iron also helps in fat metabolism and energy production.[12]
Quinoa is a great dietary source of iron, providing up to 16% of the Daily Value per serving.
Is quinoa actually a superfood?
If you remain skeptical about the true health and weight-loss value of quinoa, think that in 1993, the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) gave quinoa interest, due to its desirable food qualities for astronauts on long-duration space missions![13]
In addition, the United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) declared 2013 as the International Year of Quinoa to raise public awareness of the nutritional benefits of this durable plant in terms of food and nutrition security worldwide.
Quinoa’s nutritional capacity and adaptability to harsh climates make it a promising crop for global food security.
Compared to other grains, quinoa seeds are gluten-free and have a better-balanced ratio of proteins, fats, and carbs, higher contents of essential amino acids and are richer in several minerals.[14]

Health benefits
Due to its high antioxidant capacity, quinoa as part of a well-balanced diet may play a beneficial role in many conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, depression, cancer, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. It may alleviate the symptoms of a high-cholesterol diet and improve immunity. Quinoa might be considered a functional food for disease prevention.[2]
Is Quinoa a healthier alternative to Rice and other Grains?
Quinoa vs Rice
Quinoa is a healthier alternative to white rice. It has almost 3 times more iron and 6 times more fiber.
| Nutrient | Quinoa (1 cup cooked) | White Rice (1 cup cooked) | % DV Quinoa | % DV White Rice | % Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 120 | 159 | 7 | 10 | -24% |
| Protein | 4.4g | 2.8g | 16 | 12 | 133% |
| Carbs | 21.3g | 27.3g | 13 | 16 | -18% |
| Fiber | 2.8g | 0.5g | 14 | 2 | 560% |
| Fat | 1.92g | 0.4g | 8 | 2 | 380% |
| Manganese | 0.631mg | 0.3mg | 32 | 15 | 117% |
| Phosphorus | 152mg | 47mg | 27 | 24 | 53% |
| Magnesium | 64mg | 13mg | 21 | 5 | 75% |
| Iron | 1.49mg | 0.46mg | 16 | 2 | 257% |
| Zinc | 1.09mg | 0.8mg | 11 | 4 | 37% |
As you can see, quinoa is a good source of fiber, protein, and important vitamins and minerals, while white rice is high in carbs and low in nutrients.
Quinoa remains a much healthier food option even than brown or wild rice!
| Nutrient | Quinoa | Brown Rice | Wild Rice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 120 | 166 | 172 |
| Protein | 4.4g | 3.5g | 3.6g |
| Carbohydrate | 21.3g | 35.7g | 36.4g |
| Fiber | 2.8g | 3.5g | 2.4g |
| Fat | 1.92g | 4.2g | 1.6g |
| Manganese | 0.631mg | 5.2mg | 2.8mg |
| Phosphorus | 152mg | 86mg | 115mg |
| Magnesium | 64mg | 158mg | 93mg |
| Iron | 1.49mg | 2.7mg | 2.6mg |
| Zinc | 1.09mg | 1.9mg | 1.0mg |
Is Quinoa the best Grain for Weight Loss?
Quinoa is one of the healthiest grain options.
| Grain | Nutrient Benefits |
|---|---|
| Chia seeds | Highest in fiber, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids |
| Amaranth | Complete protein, high in fiber, iron, and magnesium |
| Buckwheat | Gluten-free, high in protein, fiber, magnesium, and manganese |
| Oats | Good source of fiber, protein, beta-glucan, iron, magnesium, and zinc |
| Quinoa | Complete protein, high in fiber, iron, magnesium, and phosphorus |
Here are the top 5 healthiest grain options and why they are considered so:
- Quinoa is a complete protein, and it is also a good source of fiber, iron, magnesium, and phosphorus. The protein content of quinoa is higher than other cereals. It has a better distribution of essential amino acids.[4]
- Chia seeds are the richest in fiber, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids of any grain. They are also a good source of calcium, magnesium, iron, and zinc. Chia seeds can be eaten plain, added to smoothies or yogurt, or used as an egg substitute in baking.
- Amaranth is a complete protein, which means it contains all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. It is also a good source of fiber, iron, and magnesium. Amaranth can be cooked like quinoa or used as flour in baking.
- Buckwheat is a gluten-free grain that is a good source of protein, fiber, magnesium, and manganese. It is also a good source of rutin, an antioxidant that may help protect against heart disease and stroke. Buckwheat can be cooked like quinoa or used as a flour in baking.
- Oats are a good source of fiber, protein, and beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that has been shown to help lower cholesterol levels. They are also a good source of iron, magnesium, and zinc. Oats are an excellent addition to a weight-loss diet plan.
| Grain | Calories | Protein (g) | Fiber (g) | Calcium (mg) | Iron (mg) | Magnesium (mg) | Manganese (mg) | Potassium (mg) | Zinc (mg) |
| Chia | 138 | 4.7 | 10.6 | 177 | 2.7 | 335 | 2.7 | 407 | 1.6 |
| Teff | 101 | 3.9 | 2.8 | 17 | 1.9 | 184 | 3.0 | 124 | 1.1 |
| Amaranth | 103 | 3.8 | 2.1 | 16 | 1.6 | 160 | 2.1 | 135 | 1.5 |
| Oats | 71 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 10 | 0.6 | 27 | 0.6 | 61 | 0.4 |
| Quinoa | 120 | 4.4 | 2.8 | 17 | 1.5 | 64 | 0.6 | 172 | 1.1 |
| Wheat | 71 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 10 | 0.6 | 25 | 0.6 | 61 | 0.4 |
| Kamut | 97 | 3.8 | 1.9 | 29 | 1.9 | 97 | 1.9 | 97 | 0.6 |
| Millet | 119 | 3.5 | 1.3 | 8 | 0.7 | 114 | 0.6 | 99 | 0.5 |
| Rye | 83 | 2.7 | 1.3 | 26 | 0.8 | 41 | 0.8 | 33 | 0.4 |
| Bulgur | 83 | 3.1 | 1.8 | 17 | 0.6 | 43 | 0.7 | 33 | 0.3 |
| Buckwheat | 92 | 3.4 | 1.5 | 10 | 1.0 | 51 | 0.6 | 114 | 0.4 |
| Rice | 130 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 10 | 0.2 | 35 | 0.2 | 61 | 0.2 |
Please note that the nutritional content of these grains may vary depending on the specific variety and preparation method.
It is recommended to consume a variety of grains to ensure that you are getting all the necessary nutrients. You can include quinoa in your diet along with other grains to reap the benefits of a diverse range of nutrients.
How much can I eat a day?
The amount of quinoa you can eat in a day depends on your individual calorie needs and dietary goals. A 1-cup serving of cooked quinoa contains only 222 calories. You could eat a serving a day as part of a balanced diet.
However, it is important to note that quinoa alone cannot lead to weight loss. To lose weight, you need to create a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories than you burn.
If you are trying to lose weight, it’s preferable to include in your eating habits a variety of whole grains. Not just quinoa. Getting a diverse range of antioxidants and other phytonutrients is far more important for good health and for building a lean body.
Can Quinoa make me fat?
To gain weight, you need to consume more calories than you burn. Quinoa is highly unlikely to make you gain weight. Using fattening foods in quinoa recipes can make you fat, though.
For example, avoid using vegetable oil or butter in your recipes. They’re two of the most calorie-dense foods you can eat, as they’re almost 100% fat. Just a tablespoon of any vegetable oil has about 125 calories!
Tips to incorporate Quinoa into your daily eating habits
Here are some tips for incorporating quinoa into your diet:
- Cook quinoa like rice. Quinoa is cooked like rice, so it’s a great way to add whole grains to your diet. Simply rinse the quinoa, bring it to a boil in water or broth, then reduce the heat and simmer until it’s tender and fluffy.
- Quinoa breakfast bowl: Combine cooked quinoa with Greek yogurt, fresh berries, and a drizzle of honey for a nutritious and filling breakfast.
- Substitute quinoa for pasta. Quinoa can be used as a substitute for pasta in many dishes. Try making quinoa lasagna, quinoa pasta salads, or quinoa stir-fries.
- Add quinoa to salads. Quinoa is a great addition to salads because it adds protein and fiber. Cook some quinoa and toss it with your favorite salad greens, vegetables, and dressing.
- Make quinoa breakfast porridge. Quinoa porridge is a warm and comforting breakfast option. Cook quinoa in milk or water, then stir in your favorite toppings, such as fruit, nuts, and seeds. My favorite way to eat quinoa is to add it to oatmeal. Instead of milk, I use kefir, which is the healthiest dairy for weight loss!

- Add quinoa to smoothies. Quinoa can be added to smoothies to add protein and fiber. Blend quinoa with your favorite fruits, vegetables, and yogurt or milk.
- Use quinoa as a thickener. Quinoa can be used as a thickener in soups, stews, and sauces. Cook quinoa and puree it until smooth, then add it to your dish.
- Make quinoa bowls. Quinoa bowls are a healthy and satisfying meal. Cook quinoa and top it with your favorite toppings, such as grilled chicken, roasted vegetables, avocado, and salsa.
- Use quinoa in baked goods. Quinoa can be added to muffins, pancakes, bread, and cookies to add protein and fiber.
- Make quinoa burgers. Quinoa burgers are a healthy and flavorful alternative to beef burgers. Mix cooked quinoa with ground vegetables, beans, and seasonings, then form into patties and cook until golden brown.
- Make quinoa snacks. Quinoa can be used to make healthy snacks, such as quinoa energy balls, quinoa granola bars, and quinoa chips.
- Try different quinoa varieties. There are many different varieties of quinoa available, each with its unique flavor and texture. Experiment with different varieties to find your favorites. They also add color to any dish!
With a little creativity, you can easily add quinoa to your diet and reap its many benefits.
How to Cook it?
Quinoa contains certain antinutrients that can hinder nutrient absorption, such as saponins and phytic acid. Tannin, trypsin inhibitor, and oxalate also inhibit nutrient absorption, but they are present only in trace amounts.
These antinutrients can bind to minerals like zinc, iron, and calcium, reducing their bioavailability. For instance, we absorb only about 0.23% of the iron of quinoa.[16]
Their negative effects are significantly reduced by germination, though. Also, germination significantly increases the total phenolic content in quinoa. The total phenolic content of red and yellow quinoa can be increased by more than 200% after 6 days of germination!
How to increase Bioavailability?
Rinsing
Rinse the quinoa thoroughly under cold water to remove any dirt or debris. Then Place it in a fine-mesh strainer and rinse it under cold running water for 2 minutes. This will remove the natural coating called saponin, which can make it taste bitter or soapy. After rinsing, drain the quinoa thoroughly to remove any excess water.
Soaking
If you want to soak it, place the rinsed quinoa in a bowl and cover it with water. The ratio of water to quinoa should be 2:1. Let the quinoa soak for at least 15 minutes, but preferably for 1-2 hours.
After soaking, drain the quinoa through a fine-mesh sieve and rinse it thoroughly under cold water for 30-60 seconds. Soaking quinoa is optional, but it can help reduce cooking time.

Sprouting
To germinate quinoa safely, soak the quinoa seeds in water for 12-24 hours to help soften the seed coat and speed up germination. Drain the water and rinse the seeds thoroughly.
Place the drained and rinsed quinoa seeds in a shallow dish or tray. Spread them out in a thin layer so that they have plenty of room to sprout. Check them periodically to make sure they remain moist.
Depending on the temperature, it will take 2-3 days for the quinoa seeds to sprout. You will know that they are ready when they have grown small, white rootlets and the sprouts are about 1-2 inches long.
Once the quinoa sprouts are ready, you can store them in the refrigerator for up to 3 days.
Rinse them thoroughly before using them.
Use organic, untreated seeds to avoid exposure to harmful chemicals.
Iron solubility increases up to 4 times after the germination of quinoa.[17]
Pairing with proper foods
Preparing quinoa recipes with vitamin C, meat, poultry, or fish could also have beneficial effects on mineral absorption.
For instance, vitamin C significantly increases the absorption of nonheme iron by up to 270%. Bell peppers, broccoli, and citrus foods are among the richest common foods in vitamin C that can be used in many quinoa dishes.
You could add honey to your quinoa oatmeal. It supports weight loss. It’s packed with antioxidants and a tbsp of honey may increase iron levels by up to 20%.
What’s the best time of the day to eat Quinoa for Weight Loss?
While there is no specific time of day that is best to eat quinoa for weight loss, you could add quinoa to your breakfast, lunch, or meals, or even use it as a snack.
However, consuming foods high in carbs earlier in the day may be better if you want to lose weight or improve blood sugar levels. This is because most Americans are active early in the day and more sedentary at night.
Having your biggest portion of carbs in the evening can cause a blood sugar spike. Your body then stores the extra glucose that you didn’t use for energy as body fat.
Dangers of eating Quinoa
Quinoa is generally considered to be safe for most people. However, some people may experience allergic reactions to quinoa. If you are allergic to other grains, you should avoid consuming quinoa before consulting your physician. It’s considered safe for people with wheat allergy, though.
However, there have been reports of allergic reactions to quinoa, including itching, hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing. These reactions are typically caused by quinoa’s saponins. Remove them by rinsing quinoa thoroughly in water before cooking.
If you have a history of food allergies, you may also want to start with a small amount and gradually increase your intake to see if you have any reactions.
Also, it is suggested to consume cooked quinoa instead of raw quinoa because certain protein toxins that can be found in quinoa are easily destroyed at high temperatures.
Why has Quinoa helped me lose weight?
I consume quinoa at least 2 to 3 times a week. Above all, it helped me control my cravings for sugary foods. I put it on my oatmeal for crunchiness and along with chia seeds, buckwheat, and oats are my favorite grains. I haven’t eaten white rice since I discovered the superior nutritional value of quinoa.
Αfter how long will I see a difference?
Saponins and other antioxidants in quinoa manage glucose responses. According to a recent study, the daily consumption of quinoa-enriched bread for 4 weeks significantly reduced blood glucose responses as well as LDL cholesterol. A daily 20-gram dose of quinoa flour was applied.[9]

Some people may see a difference in their glucose levels after only a few days, while others may take longer. Be patient and consistent. I felt more energized and less lethargic when I switched from white rice and bread to quinoa and other whole grains after about two weeks!
Is it worth the cost?
Quinoa is typically more expensive than white rice but it’s way more nutritious. If you buy quinoa in bulk, you can save money. Keep in mind that organic brown or wild rice can be more expensive than quinoa!
You can compare prices on iHerb.