Vitamin C is crucial for skin health, playing a key role in combating skin aging, wrinkles, age spots, and loss of elasticity. Taking 5-10 times the daily value of vitamin C, especially during the summer, can be highly beneficial. Combining high oral intake with topical application can work wonders for your skin’s appearance and structure!
Table of Contents
- The Key Role of Vitamin C for the Skin
- Effects of Sunlight Radiation to the Skin
- Vitamin C Protects the Skin in Summer
- How Much Vitamin C During Summer?
- Tips for Selecting Effective Vitamin C Skincare Products
- Cost-Effective Ways to Increase Vitamin C Intake
- 24 Myths about Vitamin C & Skin Health
- Other Protective Vitamins for Skin Protection

The Key Role of Vitamin C for the Skin
The Skin’s High Vitamin C Concentration: A Shield Against Damage
The skin, our largest organ, acts as a barrier between us and the world. Just like the rest of our body, its health and appearance are deeply connected to what we eat.
Our skin is made of two main layers:
- Epidermis (Outer Layer): This acts as our first line of defense, protecting us from UV radiation, harmful pathogens, and pollution. However, due to its constant exposure to the environment, the epidermis is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress, which is damage caused by free radicals.
- Dermis (Inner Layer): This layer provides support and elasticity to the skin, as well as delivering nutrients to the outer layer.
Interestingly, the epidermis has a much higher concentration of vitamin C compared to the dermis – up to five times more! This high concentration reflects the critical role vitamin C plays in protecting the outer layer from damage.[1]
When exposed to threats like UV rays, pollution, or even the natural aging process, our skin’s vitamin C levels can become depleted. This depletion can lead to increased oxidative stress, which in turn contributes to premature skin aging.
Vitamin C is Crucial for Collagen Synthesis
Collagen is a protein that forms a scaffold-like structure within the dermis (inner layer) of your skin. Imagine it as a dense network of fibers that provide support and firmness. It also plays a vital role in keeping your skin elastic. Collagen allows your skin to stretch and bounce back, preventing wrinkles and sagging.
- The dermis is rich in collagen, which makes up approximately 70-80% of its dry weight.
- The epidermis contains very little collagen compared to the dermis. Collagen is not a significant component of the epidermis, as it primarily consists of keratinocytes and a small amount of extracellular matrix.
Collagen attracts and holds onto water molecules, keeping your skin hydrated.
While your body naturally produces collagen, the process slows down with age and exposure to environmental factors like sun damage. That’s where vitamin C steps in.
Studies suggest that sufficient vitamin C intake can stimulate the production of new collagen fibers in the skin. Stronger collagen fibers thanks to vitamin C lead to a more elastic and youthful appearance.[2]
Vitamin C acts as a cofactor for enzymes called prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase. These enzymes are essential for stabilizing the collagen molecule, making it usable by the body.[3]
Additionally, vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that fights free radicals, and harmful molecules that damage collagen fibers.
Keep in mind that the body requires many compounds besides vitamin C to synthesize collagen.
Studies
- Combining exercise with vitamin C-enriched collagen supplements may stimulate the body’s natural collagen synthesis.[4]
- Preclinical research shows promise for vitamin C’s ability to accelerate bone healing following a fracture. It appears to work by increasing the synthesis of type I collagen, a crucial building block for bones, and by reducing oxidative stress, which can damage cells.[5]
Effects of Sunlight Radiation to the Skin
Sunlight, particularly its ultraviolet (UV) component, has immediate and noticeable effects on the skin.
- Exposure to UVB radiation can cause sunburn, which is an acute inflammatory response characterized by redness, swelling, and pain. Sunburn results from damage to the DNA in skin cells, leading to the release of inflammatory mediators.
- UVA radiation, while less likely to cause sunburn, penetrates deeper into the skin and can contribute to immediate tanning and long-term skin damage by affecting the dermis.
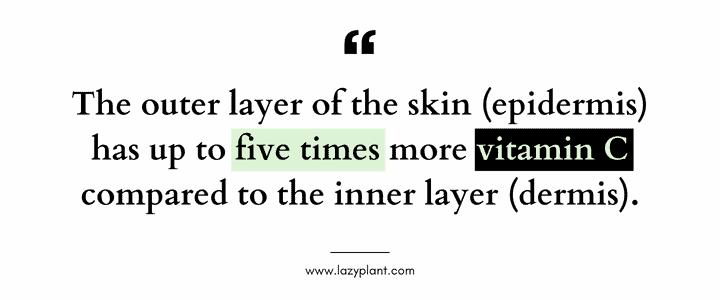
Prolonged and repeated exposure to sunlight leads to chronic skin damage known as photoaging. This process is marked by the degradation of collagen and elastin fibers in the dermis, leading to wrinkles, sagging, and a leathery texture.
UV radiation stimulates the production of free radicals, which cause oxidative stress and further degrade the skin’s structural components. Over time, the skin’s ability to repair this damage diminishes, resulting in visible signs of aging.
Increased Risk of Skin Cancer
One of the most serious effects of sunlight radiation is an increased risk of skin cancer.
Both UVA and UVB radiation can induce mutations in the DNA of skin cells, potentially leading to cancers such as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. UV radiation can cause direct DNA damage or indirect damage through the generation of reactive oxygen species. The cumulative effect of these mutations over time significantly raises the risk of developing skin cancer.[6,7]
Sunspots
Sun exposure can also lead to the formation of sunspots. UV radiation stimulates melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin color, as a natural defense mechanism.
However, uneven distribution and overproduction of melanin can result in dark spots and patches on the skin. These areas are often more pronounced with age and prolonged sun exposure.
Immune System Suppression
Another critical effect of UV radiation is its impact on the skin’s immune function. UV radiation can suppress local immune responses, making the skin more susceptible to infections and impairing its ability to detect and destroy abnormal cells. This effect on the immune responses of the skin contributes to the development and progression of skin cancers by allowing damaged cells to proliferate unchecked.
Sunlight radiation has various effects on the skin, from immediate reactions like sunburn to long-term consequences such as photoaging, sunspots, and even increased skin cancer risk.
Vitamin C Protects the Skin in Summer
How vitamin C helps protect skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation and sun damage.
May Protect from Sun Burn
Vitamin C can play a supportive role in protecting the skin from sunburn and other damage caused by UV radiation, but it should not be relied upon as the sole form of protection during sunbathing or extended sun exposure.
It helps neutralize free radicals produced by UV radiation, stimulates collagen synthesis, and even enhances the effectiveness of sunscreen. When combined with sunscreens, vitamin C can provide an additional layer of protection by neutralizing free radicals that manage to penetrate the skin.
However, vitamin C is not a substitute for sunscreen. Sunscreens contain ingredients specifically designed to block or absorb UV radiation, preventing it from penetrating the skin. Sunscreen with a high SPF should be the primary method of protection during sunbathing or extended sun exposure.
For maximum benefit, vitamin C can be used both topically and orally. Topical vitamin C serums can provide direct antioxidant protection to the skin, while oral supplements can boost the skin’s overall antioxidant capacity.
In addition to using vitamin C, other sun protection measures should include:
- seeking shade during peak UV hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.),
- wearing protective clothing, and
- reapplying sunscreen every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
Supports Wound Healing
Many studies have shown that high dosages of vitamin C from supplements or topical applications can reduce wound recovery time and inflammation. The topical application of a silicone gel with vitamin C can significantly improve the appearance of surgical scars even in the face.[8]
Impaired wound healing is a common sign of vitamin C deficiency.
May Hydrate the Skin
Vitamin C can indirectly impact skin hydration as it supports collagen production which is essential for retaining moisture and preventing transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
When the skin’s barrier is strong and intact, it is better able to hold onto moisture, thereby enhancing hydration.
Additionally, vitamin C’s antioxidant properties protect the skin from oxidative stress caused by environmental factors such as UV radiation and pollution, which can otherwise compromise the skin’s moisture barrier.
Topical Vitamin C and Skin Hydration
Topical vitamin C directly impacts skin hydration more visibly and immediately.
When applied to the skin in the form of serums or creams, vitamin C can improve moisture retention by supporting the lipid barrier and reducing water loss. The antioxidant effects of vitamin C help to soothe inflammation and redness, often associated with dehydrated skin.
Furthermore, vitamin C enhances the skin’s ability to produce natural moisturizing factors (NMFs), which are essential for maintaining skin hydration and smoothness.
Additionally, topical formulations of vitamin C often include other hydrating ingredients like hyaluronic acid, which can draw moisture into the skin and lock it in, providing a dual benefit of both hydration and protection against moisture loss.
Both oral and topical vitamin C contribute to skin hydration!
May Protect Skin Tone
Oral supplementation of vitamin C contributes significantly to overall skin health and can lead to a more even and bright skin tone. By neutralizing free radicals, vitamin C helps to prevent cellular damage that can lead to uneven skin tone and dullness.
Topical Vitamin C for Brightening Effects
Topical application of vitamin C is particularly effective for brightening the skin and improving skin tone. Vitamin C serums and creams are designed to deliver high concentrations of the nutrient directly to the skin, where it can be most effective.
When applied topically, vitamin C can inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. By reducing melanin production, vitamin C helps to fade hyperpigmentation, dark spots, and other forms of discoloration, resulting in a more even skin tone.[9,10]
Furthermore, topical vitamin C can enhance the skin’s natural radiance by promoting the exfoliation of dead skin cells. This exfoliation process reveals the newer, healthier skin underneath, giving the complexion a brighter and more youthful appearance. Many users report a noticeable improvement in skin brightness and clarity with consistent use of topical vitamin C products.[11]
Combined Approach for Optimal Results
For the best results in achieving a brighter and more even skin tone, combining oral and topical vitamin C is recommended.
Oral vitamin C supplements ensure that the body has sufficient levels of the nutrient to support overall skin health, while topical applications target specific areas of concern on the skin’s surface. This combined approach maximizes the benefits of vitamin C, addressing skin issues from both the inside and outside.
It is important to choose high-quality vitamin C products and to use them consistently for optimal results. When selecting a topical vitamin C product, look for formulations that contain stabilized forms of the nutrient, such as ascorbic acid or its derivatives, to ensure maximum efficacy.
Vitamin C, whether taken orally or applied topically, offers significant benefits for improving skin tone and achieving a brighter complexion.
Helps Recycle Vitamin E
Vitamin E, a lipid-soluble antioxidant, is primarily found in the skin’s lipid-rich areas, such as cell membranes and the stratum corneum. It protects the skin from oxidative damage by neutralizing free radicals generated by UV exposure and other environmental stressors.
However, during this process, vitamin E itself becomes oxidized and loses its antioxidant capability. This is where vitamin C steps in.
Vitamin C, being water-soluble, can effectively interact with the oxidized form of vitamin E (tocopheroxyl radical) and regenerate it back to its active antioxidant form. This regeneration process allows vitamin E to continue protecting against oxidative stress.[12]
The collaboration between these two vitamins ensures a sustained antioxidant defense mechanism in the skin, preventing damage from UV radiation, pollution, and other harmful factors.
The lipid-rich environment of the skin, where vitamin E resides, is crucial for maintaining the skin’s barrier function. By ensuring that vitamin E remains active, vitamin C helps strengthen the skin barrier, preventing moisture loss and protecting against environmental pollutants. Vitamin E also helps maintain the integrity of collagen fibers.
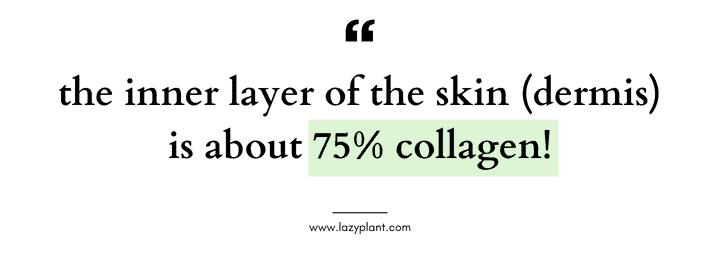
May protect from Wrinkles
Sunlight, particularly in the summer, particularly its ultraviolet (UV) component, accelerates the formation of wrinkles through mechanisms such as collagen breakdown, elastin damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation.
Vitamin C protects the skin from these effects by neutralizing free radicals, supporting collagen synthesis, reducing inflammation, and promoting skin repair.
Incorporating vitamin C into your skincare routine, along with using sun protection measures like sunscreen and protective clothing, can significantly help in preventing and reducing the appearance of wrinkles caused by sun exposure.
How Much Vitamin C During Summer?
Recommended Daily Intake
The recommended daily intake of vitamin C varies depending on age, sex, and certain health conditions.
General Population
- Adults (19+ years):
- Men: 90 milligrams (mg) per day
- Women: 75 mg per day
- Children:
- 1-3 years: 15 mg per day
- 4-8 years: 25 mg per day
- 9-13 years: 35 mg per day
- Teenagers (14-18 years):
- Boys: 75 mg per day
- Girls: 65 mg per day
Special Considerations
- Smokers: Due to increased oxidative stress, smokers have a higher need for vitamin C. The recommended daily intake for smokers is increased by 35 mg per day.
- Pregnant & Lactating Women: Pregnant women require 85 mg per day, while lactating women need 120 mg per day to support the developing baby.
- Patients with Certain Conditions: Individuals with specific medical conditions like iron deficiency anemia or undergoing dialysis might require higher vitamin C intake as recommended by their physician.
It’s important to note that these are minimum recommended intakes. Consuming more vitamin C from a healthy diet is generally safe and can offer additional health benefits.
What’s the ideal Dose during the Summer?
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for vitamin C is designed to prevent deficiency but may not be sufficient for optimal skin protection, especially during the summer when sun exposure increases oxidative stress on the skin.
While the RDA for adults is 90 mg per day for men and 75 mg per day for women, many experts suggest higher doses for enhanced skin protection and overall health benefits.
General Recommendations
For Enhanced Skin Protection: 200-500 mg per day.
For Maximum Antioxidant Support: 500-1000 mg per day, divided into two doses to maintain steady blood levels.
Applying a vitamin C serum with a concentration of 10-20% once daily can significantly enhance skin protection. Topical application delivers vitamin C directly to the skin cells where it can neutralize free radicals and support collagen production.
Most people are rather unlikely to get these high dosages from food alone. You could take vitamin C supplements. Daily doses of 1,000 mg are considered pretty safe.
Individual vitamin C requirements can vary based on factors like age, health status, lifestyle, and specific health goals. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before significantly increasing vitamin C intake, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
For optimal skin protection during the summer, higher doses of vitamin C, ranging from 200-1000 mg per day, may be beneficial.
Do I need higher amounts even if I use Sunscreen?
Yes, even if you use sunscreen, higher amounts of vitamin C can still be beneficial. While sunscreen effectively reduces UV radiation exposure, it does not completely eliminate free radicals generated by sunlight. Using vitamin C in conjunction with sunscreen can provide comprehensive protection against sun-induced skin damage.
What if I don’t Sunbathe?
Even if you don’t sunbathe, higher amounts of vitamin C can still be beneficial for overall skin health. Regular daily exposure to sunlight, even during routine outdoor activities, can generate free radicals and contribute to skin aging and damage.
Summer Foods rich in Vitamin C
You can easily get the recommended daily dose of vitamin C from your diet. 5 servings of fruits and vegetables a day can provide more than 100 mg of vitamin C.
| Category | Food | Serving Size | Vitamin C (mg) | % DV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruits | Oranges | 1 medium (131g) | 70 mg | 78% |
| Kiwi | 1 medium (69g) | 71 mg | 79% | |
| Mangoes | 1 cup (165g) | 60 mg | 67% | |
| Pineapple | 1 cup (165g) | 79 mg | 88% | |
| Papaya | 1 cup (140g) | 88 mg | 98% | |
| Watermelon | 1 cup (152g) | 12 mg | 13% | |
| Cantaloupe | 1 cup (177g) | 58 mg | 64% | |
| Vegetables | Red Bell Peppers | 1 medium (119g) | 152 mg | 169% |
| Tomatoes | 1 medium (123g) | 17 mg | 19% | |
| Broccoli | 1 cup, raw (91g) | 81 mg | 90% | |
| Spinach | 1 cup, raw (30g) | 8 mg | 9% | |
| Kale | 1 cup, raw (67g) | 80 mg | 89% | |
| Snow Peas | 1 cup, raw (98g) | 60 mg | 67% | |
| Summer Squash | 1 cup, raw (124g) | 21 mg | 23% | |
| Herbs | Parsley | 1/4 cup (15g) | 20 mg | 22% |
| Berries | Blueberries | 1 cup (148g) | 14 mg | 15% |
| Raspberries | 1 cup (123g) | 32 mg | 36% | |
| Strawberries | 1 cup (152g) | 89 mg | 99% |
Tips for Selecting Effective Vitamin C Skincare Products
Factors to Consider
When selecting effective vitamin C skincare products, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure you’re getting the most benefit from the product.
Check the Form of Vitamin C
- L-ascorbic acid is the purest and most effective form of vitamin C, but it can be unstable.
- Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate and Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate are stable and less irritating derivatives, suitable for sensitive skin.
- Ascorbyl Glucoside and Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate are forms that are also stable and work well for various skin types.
Look at the Concentration
- 10-20%: For L-ascorbic acid, a concentration between 10-20% is ideal for effective results without causing irritation.
- 5-10%: For more stable derivatives, lower concentrations can still be effective and gentle on the skin.
Check the pH Level
3.0-3.5: L-ascorbic acid works best at a lower pH level of around 3.0-3.5. Higher pH levels may decrease its effectiveness.
Packaging Matters
Vitamin C is sensitive to light and air, so choose products in opaque and airtight packaging to prevent oxidation. Pump bottles or tubes also help limit exposure to air compared to jars or open containers.
Additional Ingredients
- Vitamin E and ferulic acid are antioxidants that can enhance the stability and effectiveness of vitamin C.
- Hyaluronic acid helps with hydration and can improve the delivery of vitamin C into the skin.
- Peptides can complement the anti-aging effects of vitamin C.
Check Expiry Date
Vitamin C products can degrade over time. Always check the expiry date and store it in a cool, dark place.
Consider Your Skin Type
- Sensitive Skin: Opt for derivatives like Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate or Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate, which are gentler.
- Oily Skin: L-ascorbic acid in a lightweight, non-greasy formula is ideal.
- Dry Skin: Look for vitamin C products with added moisturizers like hyaluronic acid.
Read Reviews and Research Brands
Choose products from reputable brands known for quality skincare formulations. Check customer reviews to see real-world results and any potential issues with the product.
44M+ reviews
iherb.com
offers thousands of vitamin C supplements and serums.
Patch Test First
Apply a small amount on your forearm or behind your ear to check for any adverse reactions before using it on your face.
If you have specific skin concerns or conditions, consult with a dermatologist to recommend the best vitamin C product for your needs.
Vitamin C serum doesn’t replace sunscreen. Use SPF 30 or higher broad spectrum protection every day.
Potential Side Effects & Sensitivities of Vitamin C Serum
While vitamin C serums offer numerous benefits for the skin, there are potential side effects and sensitivities to be aware of. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
Potential Side Effects
Some individuals may experience redness, itching, or a slight burning sensation, especially with high concentrations of L-ascorbic acid. Vitamin C can sometimes lead to dryness or flakiness, particularly if used in conjunction with other active ingredients.
Allergic reactions can manifest as hives, rashes, or more severe skin irritation. This is more likely if the product contains additional ingredients like fragrances or preservatives that can trigger allergies.
While vitamin C itself is an antioxidant and can help protect against UV damage, it can also make the skin more sensitive to sunlight. It’s essential to use sunscreen during the day when using vitamin C serums.
Moreover, some people might experience an increase in breakouts, particularly if they have oily or acne-prone skin. This can happen due to the serum’s formulation or if the skin is not properly adjusted to the new product.
Sensitivities
Serums with vitamin C concentrations above 20% can be more irritating and may not provide additional benefits compared to those with 10-20% concentration.
L-ascorbic acid is potent but can be more irritating for sensitive skin. Derivatives like Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate and Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate are gentler options.
Products with a low pH (around 3.0-3.5) are more effective but can cause irritation. A slightly higher pH (around 5-6) may be better tolerated by sensitive skin.
Managing Side Effects & Sensitivities
Always do a patch test by applying a small amount of serum on the forearm or behind the ear and wait for 24-48 hours to check for any adverse reactions. Begin with a lower concentration and gradually increase as your skin builds tolerance. Start by using the serum every other day and then move to the daily application if tolerated well.
Use a good moisturizer to counteract any dryness or flakiness caused by the serum. Hyaluronic acid-based moisturizers are a good complement.
Be cautious when using vitamin C with other potent active ingredients like retinoids, AHAs/BHAs, or benzoyl peroxide, as these combinations can increase irritation.
Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen during the day to protect against increased sun sensitivity.
If you have sensitive skin, specific skin conditions, or experience severe reactions, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and product recommendations.
QUIZ
Cost-Effective Ways to Increase Vitamin C Intake
Increasing your vitamin C intake doesn’t have to be expensive. Here are some cost-effective ways to ensure you’re getting enough of this essential nutrient:
Choose Seasonal Fruits and Vegetables
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits are often less expensive when bought in season.
- Strawberries: These are rich in vitamin C and can be cost-effective, especially when purchased in bulk or during peak season.
- Kiwifruit: Often reasonably priced, kiwis are a great source of vitamin C.
Opt for Frozen Produce
Frozen strawberries, blueberries, and mixed vegetables retain their vitamin C content and can be more affordable than fresh options, especially when out of season. Also, canned goods can be a cheaper alternative and still provide a decent amount of vitamin C. Look for options with no added salt or sugar.
Grow Your Own
If you have the space, consider growing your own vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables like bell peppers, tomatoes, and strawberries. Even a small herb garden can include parsley, which is high in vitamin C. Fresh parsley and thyme are also high in vitamin C and can be grown at home or bought at a low cost. Add them to meals for a nutritional boost.
Buy in Bulk
Buying fruits and vegetables in bulk from wholesale stores or local markets can reduce the overall cost. Make sure to store them properly to avoid spoilage. If you buy in bulk or grow your own produce, freeze or can the excess to extend its shelf life and ensure a steady supply of vitamin C-rich foods.
Incorporate Budget-Friendly Sources
Examples of cost-effective vitamin C-rich foods:
| Food | Serving Size | % DV per Serving |
|---|---|---|
| Oranges | 1 medium | 78% |
| Strawberries | 1 cup | 108% |
| Broccoli | 1 cup, cooked | 135% |
| Bell Peppers (Red) | 1 medium | 169% |
| Kiwi | 1 medium | 71% |
| Cabbage | 1 cup, cooked | 54% |
| Potatoes | 1 medium | 28% |
| Spinach | 1 cup, raw | 9% |
Take Advantage of Sales and Discounts
Look for sales, discounts, and coupons for fruits and vegetables at local grocery stores. Keep in mind that prices can be lower at farmers markets, especially near closing time when vendors might offer discounts.
Cook Smart
Some cooking methods can reduce vitamin C content. Steaming vegetables or eating them raw can help preserve their vitamin C levels. Additionally, you could make your own vitamin C-rich smoothies and juices using affordable ingredients like oranges, spinach, and frozen berries.
DIY Vitamin C Masks
Creating your own vitamin C face masks at home can be an effective and affordable way to enhance your skincare routine. Here are some simple DIY vitamin C mask recipes you can try:
Lemon and Honey Mask
Ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon lemon juice (rich in vitamin C)
- 1 tablespoon honey (for its moisturizing properties)
Instructions:
- Mix the lemon juice and honey in a small bowl.
- Apply the mixture to your face, avoiding the eye area.
- Leave it on for 15-20 minutes.
- Rinse off with lukewarm water and pat your skin dry.
Orange Peel Powder Mask
Ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon orange peel powder (rich in vitamin C)
- 1 tablespoon yogurt (for its lactic acid and hydration)
Instructions:
- Mix the orange peel powder and yogurt to form a paste.
- Apply the paste evenly to your face.
- Leave it on for 15-20 minutes.
- Rinse off with lukewarm water and pat your skin dry.

Vitamin C Tablet Mask
Ingredients:
- 1 vitamin C tablet (crushed into a fine powder)
- 2 tablespoons aloe vera gel (for its soothing properties)
Instructions:
- Crush the vitamin C tablet into a fine powder.
- Mix the powder with aloe vera gel to form a smooth paste.
- Apply the paste to your face.
- Leave it on for 15-20 minutes.
- Rinse off with lukewarm water and pat your skin dry.
Strawberry and Yogurt Mask
Ingredients:
- 2-3 ripe strawberries (rich in vitamin C)
- 1 tablespoon yogurt (for its lactic acid and hydration)
Instructions:
- Mash the strawberries into a smooth pulp.
- Mix the strawberry pulp with yogurt.
- Apply the mixture to your face.
- Leave it on for 15-20 minutes.
- Rinse off with lukewarm water and pat your skin dry.
Tips for Using DIY Vitamin C Masks:
- Patch Test: Always do a patch test on a small area of your skin before applying the mask to your face to ensure you don’t have an allergic reaction.
- Use Fresh Ingredients: For the best results, use fresh ingredients and make the mask just before application.
- Sun Protection: Vitamin C can make your skin more sensitive to the sun, so always apply sunscreen during the day.
- Storage: If you have leftover mask mixture, you can store it in the refrigerator for up to a week. However, fresh masks are always more effective.
- Frequency: Use these masks 1-2 times a week to avoid over-exfoliation and to give your skin a regular vitamin C boost.
24 Myths about Vitamin C & Skin Health
Myth: Vitamin C Only Comes from Citrus Fruits Reality: Vitamin C is found in a variety of fruits and vegetables, including strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
Myth: Vitamin C Can Replace Sunscreen Reality: While vitamin C offers some protection against UV damage, it cannot replace sunscreen and should be used in conjunction with it.
Myth: Higher Doses of Vitamin C Are Always Better Reality: Excessive vitamin C can lead to irritation and has diminishing returns for skin benefits beyond a certain point.
Myth: Vitamin C Causes Skin Sensitivity Reality: Vitamin C can be sensitizing for some, but many people can use it without any issues if it’s formulated correctly and used appropriately.
Myth: Vitamin C Only Benefits Mature Skin Reality: Vitamin C is beneficial for all skin types and ages, helping with the prevention and repair of damage.
Myth: All Vitamin C Serums Are the Same Reality: The effectiveness of a vitamin C serum depends on its form, concentration, and formulation stability.
Myth: Vitamin C Lightens Skin Dramatically Reality: Vitamin C can help brighten the skin and reduce hyperpigmentation, but it doesn’t bleach or lighten skin dramatically.
Myth: Vitamin C Can Be Mixed with Any Skincare Ingredient Reality: Some ingredients, like niacinamide and certain acids, can reduce the effectiveness of vitamin C if not properly formulated together.
Myth: Vitamin C Benefits Are Immediate Reality: It can take weeks to months of consistent use to see significant improvements in skin health.
Myth: Vitamin C is Ineffective in Small Concentrations Reality: Even lower concentrations of vitamin C can provide antioxidant benefits and support skin health.
Myth: Vitamin C Can’t Penetrate the Skin Reality: Properly formulated vitamin C products can penetrate the skin and exert their effects effectively.
Myth: Vitamin C Is Useless Once Oxidized Reality: While oxidation reduces efficacy, slightly oxidized vitamin C can still offer some benefits.
Myth: Vitamin C Is Only for Skin Brightening Reality: Vitamin C also helps with collagen production, reducing inflammation, and protecting against environmental damage.
Myth: You Can Get Enough Vitamin C from Diet Alone for Skin Benefits Reality: Topical vitamin C can provide targeted benefits that dietary vitamin C alone cannot.
Myth: Vitamin C Causes Acne Reality: Vitamin C is non-comedogenic and can actually help reduce acne and inflammation in many cases.
Myth: Vitamin C Should Be Applied Only at Night Reality: Vitamin C can be used during the day to provide antioxidant protection against environmental damage.
Myth: Vitamin C Can Be Applied Right Before Sun Exposure Reality: While it provides some protection, it’s best to apply vitamin C under sunscreen and not rely on it alone for sun protection.
Myth: Vitamin C Needs to Be Refrigerated Reality: Some formulations do benefit from refrigeration, but many are stable at room temperature if properly formulated.

Myth: All Forms of Vitamin C Are Equal Reality: There are different forms of vitamin C, like ascorbic acid and its derivatives, each with varying stability and efficacy.
Myth: Vitamin C Thins the Skin Reality: Vitamin C supports collagen production, which can actually thicken and strengthen the skin over time.
Myth: Vitamin C Can Replace Retinoids Reality: While both are beneficial, vitamin C and retinoids have different functions and are often best used together.
Myth: Vitamin C Products Are Always Expensive Reality: Effective vitamin C products are available at a range of price points, and not all high-priced products are superior. You can find high-quality vitamin C serum for less than $15!
Myth: Vitamin C Irritates All Sensitive Skin Types Reality: Some people with sensitive skin can tolerate certain forms of vitamin C, such as magnesium ascorbyl phosphate, which are less irritating.
Myth: Vitamin C Works the Same for Everyone Reality: Individual skin types and conditions can affect how well vitamin C works, and people may experience different results.
Other Protective Vitamins for Skin Protection
In addition to vitamin C, several other vitamins play crucial roles in protecting and maintaining skin health.
Vitamin E
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals and environmental stressors, such as pollution and UV radiation.
- Moisturization: It supports the skin’s barrier function, preventing moisture loss and keeping the skin hydrated.
- Healing Properties: Vitamin E aids in wound healing and can help reduce the appearance of scars.
Vitamin A
- Cell Turnover: Vitamin A, in the form of retinoids, promotes cell turnover, helping to rejuvenate the skin and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, improving skin elasticity and reducing sagging.
- Acne Prevention: Retinoids can help prevent acne by keeping pores clear and reducing inflammation.
Vitamin D
- Skin Repair and Growth: Vitamin D plays a role in skin cell growth and repair, and can help in the treatment of psoriasis.
- Immune Function: It supports the skin’s immune system, helping to fight off infections and maintain overall skin health.
- Anti-Inflammatory: Vitamin D has anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe irritated skin.
It’s tricky to get high amounts of vitamin D from your diet. Only eggs are everyday food that contains high amounts!
Vitamin K
- Healing and Blood Clotting: Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and helps in the healing process of wounds and bruises.
- Dark Circles Reduction: It can help reduce the appearance of dark circles under the eyes by aiding in blood circulation.
B Vitamins
- Skin Barrier Function: B vitamins, especially niacin (vitamin B3), help maintain the skin’s lipid barrier, preventing moisture loss and keeping the skin hydrated.
- Reduces Redness and Inflammation: Niacinamide (a form of vitamin B3) can reduce redness, inflammation, and even out skin tone.
- Supports Cell Metabolism: B vitamins are crucial for energy production in cells, supporting overall skin health and vitality.
Incorporating these vitamins into your skincare routine through diet, supplements, or topical applications can significantly enhance skin protection and overall health.
Vitamins that protect the skin:
- Vitamin E: Antioxidant, moisturizer, healer.
- Vitamin A: Cell turnover, collagen production, acne prevention.
- Vitamin D: Skin repair, immune support, anti-inflammatory.
- Vitamin K: Healing, reduces dark circles.
- B Vitamins: Barrier function, reduces redness, supports cell metabolism.
- Vitamin B5: Moisturizing, healing.
Selenium
Selenium protects the skin from sunlight damage, due to its powerful antioxidant properties. It can neutralize UV radiation-induced free radicals that age the skin!
Selenium is involved in the synthesis of certain antioxidant enzymes, such as glutathione peroxidase and thioredoxin reductase, which are present in epidermal keratinocytes. Keratinocytes are the primary cell types found in the outer layer of the skin, called epidermis. They are about 90% of the epidermal skin cells. Selenium plays a key role in keratinocyte growth and function.[13,14]
Moreover, selenium protects the skin from inflammation. For instance, selenium can help people with psoriasis, which is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that affects about 2-3% of the population worldwide.
It’s pretty common for people with psoriasis to have low glutathione peroxidase levels. High doses of selenium can improve disease outcomes!
The recommended daily intake of selenium is 55 mcg. Even higher doses may be beneficial for the skin, though. Especially, if you’re deficient in selenium.
However, we shouldn’t get more selenium than the maximum safe dose. Too much selenium may be bad for the skin. For instance, symptoms of excessive selenium include lesions of the skin or skin rashes.[15]
Resveratrol
According to studies, a diet high in resveratrol can significantly improve multiple aging-associated parameters, such as increased skin hydration, skin elasticity, decreased skin roughness and wrinkle depth as well as lightening of age spots.[16]
Resveratrol found mainly in grapes, peanuts, and berries, has powerful anti-photoaging effects. It protects from wrinkle formation, due to exposure to UV radiation.
Moreover, grapes contain many other antioxidant compounds, which act synergistically, to protect the skin from aging. For instance, grapes have a high phenolic, anthocyanin, and flavonoid content. These compounds have a protective effect on wrinkle formation.[17]
Additionally, the unique compounds in grapes promote wound healing. Reducing the wound healing time lowers the risk of infection.
Topical application of grape seed extract results in contraction and closure of the skin wound. It releases endothelial growth factors and has antioxidant and antibacterial properties.[18,19]
The topical application of grape seed extract can repair wounds much faster! According to a study, surgical wounds treated with grape seed extract were completely repaired on day 8. Six days sooner than wounds treated with a placebo!
Most noteworthy, grape seed extract is pretty rich in proanthocyanidins.
First, these antioxidant compounds trigger the release of vascular endothelial growth factor. Moreover, they cause wound contraction and closure.
Proanthocyanidins are 20 times more powerful than vitamin C and 50 times more powerful than vitamin E.
These antioxidant compounds protect from oxidative stress, as they neutralize the dangerous free radicals. Oxidative stress may cause cell and DNA damage.
Scientists found that topical application of grape seed extract increases cell density and deposition of connective tissue, as well as improving cellular structure in the wound.
Last, but not least, grape seed extract has anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial properties, which are effective in wound healing.