A daily magnesium dose of 400 mg from food is beneficial for weight loss. Also, obese people with low levels of magnesium could burn belly fat and improve body composition by taking extra 100-250 mg of magnesium from supplements. Magnesium is good for weight loss, as it:
- regulates glucose metabolism
- improves insulin sensitivity
- builds muscle mass
- prevents water retention
- is vital for the natural synthesis of testosterone
Magnesium for Weight Loss
Magnesium is involved in more than 300 metabolic reactions in the body. For instance, magnesium is involved in nerve and muscle function, heart rhythm, blood pressure, calcium absorption, cortisol secretion, and bone health.[1,2]
It seems that overweight people who want to lose weight should follow a diet rich in magnesium. Obese people tend to have significantly lower serum magnesium levels as compared to people with a healthy body weight. In fact, low levels of magnesium have been linked to a higher BMI (Body Mass Index).[3]
Above all, magnesium plays a crucial role in determining the weight of a person because it regulates enzymatic processes and glucose metabolism. Moreover, magnesium is involved in insulin homeostasis. It improves insulin sensitivity.[4]
Actually, balancing blood sugar plays a key role in weight loss. Keeping low postprandial glucose levels supports weight loss. Low glucose levels regulate appetite.
Seeds and nuts which are the best dietary sources of magnesium have a pretty low glycemic index. They reduce hunger and lower the total glycemic load of a meal. Hence, the best time to eat almonds, walnuts, or other nuts and seeds is before a high-calorie meal or in the morning!
May Support a Lean Body
In addition, magnesium plays a key role in energy production and energy storage. Thus, athletes, in particular, require high magnesium intakes.
Furthermore, magnesium is necessary for the natural synthesis of testosterone. Testosterone is good for muscle growth and decreased percentage of body fat. Increased muscle mass has been linked to a higher metabolism and improved insulin sensitivity.
High levels of magnesium can significantly decrease systolic blood pressure at rest and during recovery from exercise. Both for aerobic and resistance exercise. Additionally, magnesium supplements seem to decrease lactate production and help athletes jump higher!
Supplement manufacturers claim that magnesium supplements can improve athletic performance because it helps lactate to be used for energy. Further scientific research is needed, though.
Magnesium deficiency can cause muscle contractions, cramps, and lead to inflammations and increased muscle recovery time.
Young athletes should be extra cautious about their daily magnesium intake, as magnesium deficiency can lead to weak bones. Magnesium is necessary for calcium absorption.
Bone Health & Obesity
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, can indirectly lead to weight gain over time. As bone density decreases, individuals may experience pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving. This can lead to a more sedentary lifestyle, reducing physical activity and calorie burn.
The risk of fractures associated with osteoporosis can make individuals more cautious and less likely to engage in physical activities, contributing to weight gain.
Osteoporosis can also lead to muscle loss, which further reduces physical activity levels and metabolic rate.
Moreover, some medications used to treat osteoporosis can have side effects like weight gain or increased appetite.
Magnesium plays a key role in bone health. First, about 60% of total body magnesium is stored in the bones.[5]
Magnesium helps increase bone mineral density because it affects the concentrations of parathyroid hormone and the active form of vitamin D. Both are vital for bone mineralization.[6]
Furthermore, low magnesium may lead to osteoporosis, as it leads to the formation of large but fragile crystals in bone tissue, significantly affecting its structure. It can reduce the vascular supply of bones.
Additionally, low magnesium may increase inflammatory cytokines, which can trigger pathologic bone remodeling and osteopenia.[7]
According to studies, women with osteoporosis have lower serum magnesium levels than women who don’t have osteoporosis. Thus, magnesium deficiency might be a risk factor for osteoporosis!
How much magnesium a day is beneficial for osteoporosis?
Women should have normal levels of magnesium in order to decrease the risk of osteoporosis.
Researchers have used magnesium dosages between 290 mg and 1,830 mg a day for a month with great results. High magnesium doses for a short period of time could help postmenopausal women with osteoporosis decrease bone loss if they’re deficient in magnesium.[8]
We should get adequate amounts of many other compounds in order to strengthen our bones. Calcium, copper, zinc, selenium, iron, fluoride, vitamins A, B, C, D, E, folate, flavonoids, and phytoestrogens are all important for increased bone mineral density and preventing osteoporosis.
Water Retention
Furthermore, magnesium can help reduce water retention. According to a study, a daily dose of 200 mg from supplements reduced the symptoms of water retention and pain in women with premenstrual syndrome.[9,10]
Another beneficial nutrient for reducing water retention and weight loss is vitamin B6.
Gut Health
Magnesium supports gut health by maintaining a balanced microbiome. Researchers found that replenishing proper magnesium levels reduces harmful bacteria involved in inflammation and associated with human diseases. For example, it can restore a beneficial intestinal flora in IBD patients.[11]
Certain gut bacteria play a role in weight management, and magnesium may positively impact this balance.
Gut bacteria impact energy metabolism. Different bacterial strains have diverse functions. Some promote the breakdown of carbs and fats for energy, while others favor their storage as fat.
Having a “good” balance of bacteria, with more “energy-burning” strains, can help you burn more calories and potentially contribute to weight loss.
Gut bacteria influence satiety and appetite. Gut microbes produce hormones like leptin and ghrelin, which regulate hunger and fullness. A healthy gut microbiome may promote the production of satiety hormones and suppress appetite-stimulating ones, leading to you feeling fuller for longer and consuming fewer calories overall.
Besides, obesity, imbalances in gut microbiota may cause a variety of negative health outcomes, including anxiety or depression, which can further affect your weight-loss efforts.[12]
By incorporating prebiotics (food for good bacteria) like fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, probiotics (supplements or fermented foods), and maintaining a balanced diet, you can nurture a healthy gut microbiome. This can potentially support weight loss efforts by optimizing metabolism, regulating appetite, and reducing inflammation.
The richest common food in probiotics is kefir.
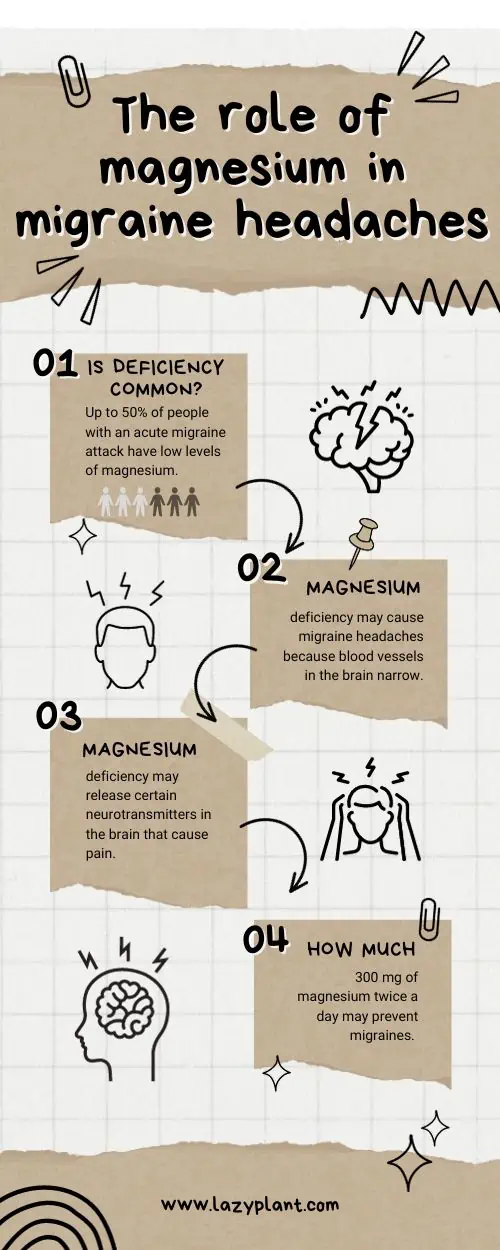
Migraine Headaches
Researchers have found that people who experience migraine headaches have lower levels of both serum and tissue magnesium. Magnesium deficiency may cause headaches because:[13,14]
- blood vessels in the brain narrow
- certain neurotransmitters in the brain that cause pain are released
Studies have shown that taking 300 mg of magnesium twice a day can prevent migraines. Moreover, the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society say that magnesium supplementation is probably effective for migraine prevention.[15]
People with regular migraine headaches tend to have lower serum magnesium levels than people with no migraine problems.[16]
It’s estimated that up to 50% of migraine patients are deficient in magnesium![17]

How much Magnesium per Day?
The recommended daily intake of magnesium from natural sources is 310-360 mg for women and 400-420 mg for men.
In fact, magnesium deficiency is common. Poor diet, carbonated beverages, age, certain gastrointestinal diseases, type 2 diabetes, as well as high intakes of calcium and fat, can cause low levels of magnesium, and lead to obesity.
If you have low levels of magnesium, taking magnesium supplements may have beneficial effects on weight loss.
Magnesium supplementation seems to cause a reduction in Body Mass Index (BMI) and waist circumference in magnesium-deficient individuals.[13]
Also, obese people may improve their metabolic profiles, blood pressure, fasting glucose and triglyceride levels after treating magnesium deficiency. More studies are needed to clearly show a link between serum magnesium levels and obesity, though.[14]
So, obese people with low levels of magnesium who want to lose weight could benefit from taking extra magnesium from supplements. In most cases, an extra magnesium dosage of 100-250 mg per tablet is more than enough for weight loss. Above all, we should get the recommended daily intake from food, which is nearly 400 mg.
You can find a wide variety of magnesium supplements on iHerb.
How much magnesium for an Athlete?
Athletes require higher doses of magnesium than the recommended daily intake. Strenuous exercise increases magnesium losses. It is estimated that exercise may increase magnesium requirements by 10-20%. Adult male athletes may need a daily magnesium dose of 500 mg, while female athletes a dose of 380 mg. Only in extreme conditions, athletes may need higher doses.[15]
Athletes who follow extreme diets for weight loss should be very cautious with their magnesium intake. They’re more vulnerable to magnesium deficiency!
Athletes with magnesium deficiency may benefit from taking magnesium supplements. Athletes shouldn’t take more than 350 mg of magnesium from supplements per day. Higher doses may cause side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. Athletes who need extra magnesium should prefer chelated supplements. They’re more easily absorbed by the body.
Common symptoms of acute magnesium deficiency are loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, weakness, numbness, tingling, muscle contractions, cramps, seizures, and abnormal heart rhythms.
Foods high in Magnesium
Nuts, seeds, beans, whole grains, and leafy greens are the best dietary sources of magnesium.
| magnesium (mg) | magnesium (mg) | ||
| pumpkin seeds | 550 | spinach | 79 |
| chia seeds | 392 | kale | 47 |
| flaxseeds | 392 | lentils | 47 |
| sesame seeds | 346 | wheat bread | 41 |
| almonds | 279 | barley bread | 41 |
| cashews | 260 | rice, brown, cooked | 39 |
| peanuts | 178 | raisins | 32 |
| black beans | 171 | avocado | 29 |
| walnuts | 158 | leeks | 28 |
| oats | 138 | bananas | 27 |
| kidney beans | 138 | potatoes, boiled | 24 |
| sunflower seeds | 129 | Brussels sprouts | 23 |
The richest common food in magnesium is pumpkin seeds.
Nuts are Excellent Sources
| magnesium (mg) per 100g | magnesium (mg) per serving | % DV | |
| almonds | 270 | 77 | 18% |
| cashews | 260 | 74 | 18% |
| pine nuts | 251 | 71 | 17% |
| hazelnuts | 173 | 49 | 12% |
| peanuts | 171 | 48 | 12% |
| walnuts | 158 | 45 | 11% |
| pecans | 121 | 34 | 8% |
| pistachios | 121 | 34 | 8% |
| macadamia nuts | 118 | 33 | 8% |
| chestnuts | 74 | 21 | 5% |
| Brazil nuts | 1.2 | 0 | 0% |
It’s estimated that we absorb 30-50% of the magnesium in food. The absorption rate depends on the consumed dose. Higher doses of magnesium are associated with lower absorption rates.[2]
Vegetables
When it comes to magnesium content, spinach stands out as one of the richest vegetables. A cup of cooked spinach provides approximately 157 mg of magnesium.
Swiss chard follows closely, offering 151 mg of magnesium per cup. Other magnesium-rich vegetables include lima beans, acorn squash, and kale.
Fruits
Among fruits, dried figs take the lead, providing an impressive 101 mg of magnesium per cup.
Avocados, bananas, and guavas also contribute to your daily magnesium intake.
Bananas are the richest common fruit in magnesium per calorie. They provide 804 mg (17% DV) per 200 calories. Avocados provide 606 mg (13% DV) while guavas provide 1,226 mg (26% DV) of magnesium per 200 calories!
Always consult your healthcare provider before taking any supplement or changing your diet.

What foods Inhibit Magnesium Absorption?
Phytate-rich foods, such as tea and beans, high doses of zinc or vitamin D from supplements, smoking, drinking too much alcohol, certain diseases, and aging can inhibit magnesium absorption.
Nuts & beans may inhibit the absorption of magnesium
Certain compounds in plant-based foods, such as cellulose and phytate can inhibit the absorption of magnesium. Cellulose is a type of insoluble fiber. Phytate or phytic acid is an anti-nutrient compound.[16]
As a rule of thumb, avoid taking magnesium supplements with vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and fruits, as these foods are high in cellulose and phytate. Green tea and dark coffee are also high in phytate.
However, you can decrease the phytate content of beans and nuts by soaking them. Soaking and rinsing beans and nuts significantly improves the absorption rate of magnesium as well as other minerals.
Zinc & vitamin D supplements may cause magnesium depletion
Also, high amounts of zinc can interfere with magnesium absorption and disrupt the magnesium balance in the body. However, we have to get extremely high dosages of zinc (142 mg per day) to inhibit magnesium absorption. We can get these amounts only from dietary supplements, or consuming too many oysters. Healthy people can’t possibly consume too much zinc from food.[17]
Furthermore, long-term high dosages of vitamin D from supplements can induce severe depletion of magnesium. Therefore, if you take vitamin D supplements, you should regularly check your vitamin D and magnesium levels.[18]
However, we should have normal vitamin D levels for optimal absorption of magnesium. In fact, vitamin D at normal levels may enhance magnesium absorption. However, as vitamin D deficiency is pretty common, many people would benefit from taking high amounts of vitamin D from dietary supplements.[19]
Smoking, alcohol & drugs are bad for magnesium absorption
Moreover, cigarette smoking can also cause magnesium deficiency. First, smoking may cause decreased appetite. Thus, smokers get less magnesium from food. Moreover, smoking may cause disturbances in the functions of the digestive system, reducing magnesium absorption as well as other minerals.[20]
Chronic alcoholism, certain health conditions, and certain medications can lead to magnesium deficiency as well.
Aging also increases the risk of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium absorption from the gut decreases with age, while renal magnesium excretion increases! Furthermore, elderly people are more likely to have chronic diseases or take medications that negatively affect the magnesium status of the body.
Maximum Safe Dose
There isn’t a maximum safe dose of magnesium from food. We can’t get too much magnesium from diet. Healthy people excrete excess magnesium in the urine.
However, excess magnesium from dietary supplements can cause side effects. Thus, the Food and National Board has established a maximum safe dose of magnesium from supplements.
In fact, the maximum safe dose of magnesium from dietary supplements for healthy adults, teenagers, and children older than 9 years is 350 mg a day. The maximum safe dosage of magnesium from supplements is only 110 mg for 4–8 years old children.
Side effects of getting too much magnesium
Diarrhea, nausea, abdominal cramps, and facial flushing are the most common side effects of too much magnesium from dietary supplements.
If you have a sensitive stomach, you better avoid certain magnesium forms, such as carbonate, chloride, gluconate, and oxide. They are more likely to upset you.
On the other hand, magnesium in the aspartate, citrate, and lactate forms is better absorbed.
Furthermore, extremely high amounts of magnesium may cause severe side effects, such as vomiting, sleepiness, muscle weakness, depression, extreme low blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, and more.
Moreover, patients with certain disease, such as impaired renal function, should consult their physician before taking magnesium supplements or changing their diet. Their kidneys can’t remove excess magnesium as effectively.
Do I need Supplements?
Unfortunately, approximately half of the US population consumes less than the recommended daily intake of magnesium. Poor diet is the main reason of low magnesium intake.[21]
Furthermore, soil is depleted of minerals, due to modern intensive agriculture technics. Hence, crops contain less magnesium than they used to be.
Also, processed foods and demineralized water contribute to magnesium deficiency. Actually, about 10% of the daily magnesium requirement is derived from water.
Consuming many foods high in magnesium is enough for healthy people. In cases of poor diet, pregnancy, or strenuous exercise, magnesium supplementation might be beneficial. Also, magnesium supplementation could be beneficial for people with low levels of magnesium.
Do supplements exceed the maximum daily safe dose?
Most dietary supplements contain 100-1,000 mg of magnesium per tablet. Hence, many dietary supplements exceed the maximum safe dose of magnesium.
As a rule of thumb, you shouldn’t exceed the maximum daily dose of 350 mg. You could take higher doses, only under medical advice.
You can find a wide variety of magnesium supplements on iHerb.